Build a Context Retrieval Layer Across Apps and Databases
...a popular interview question (explained visually).
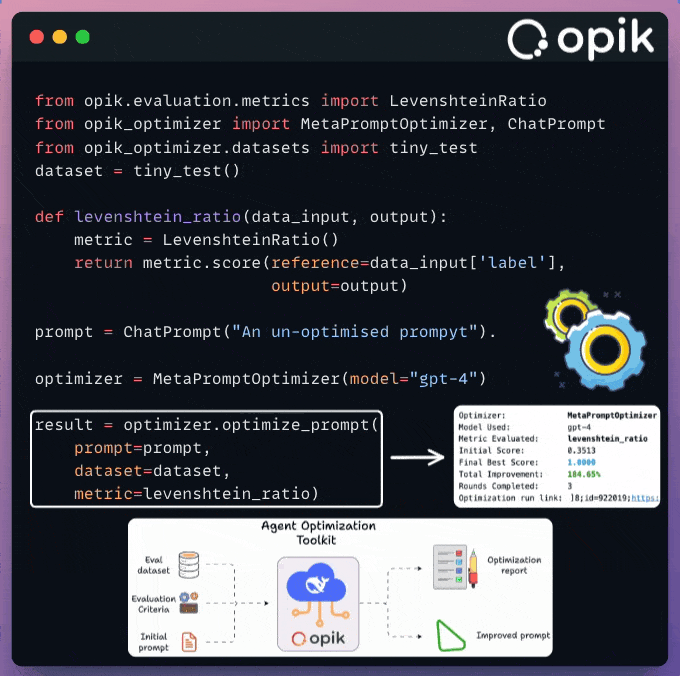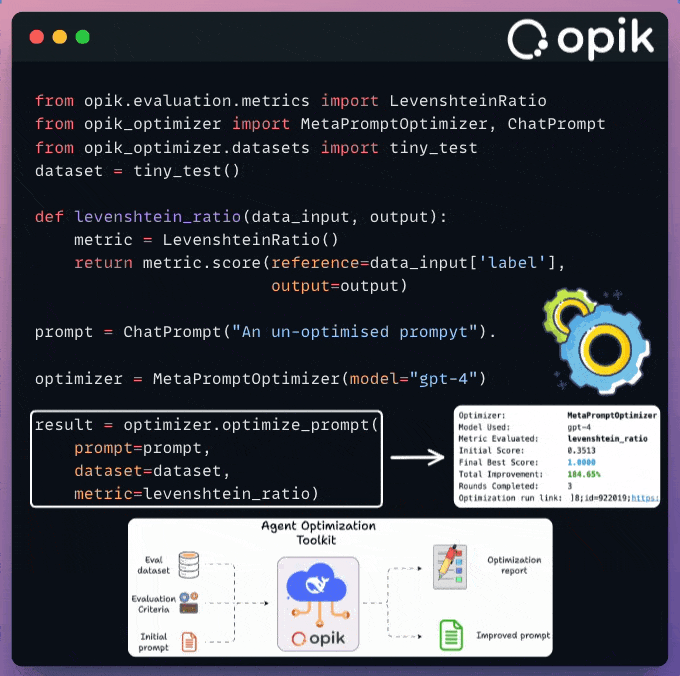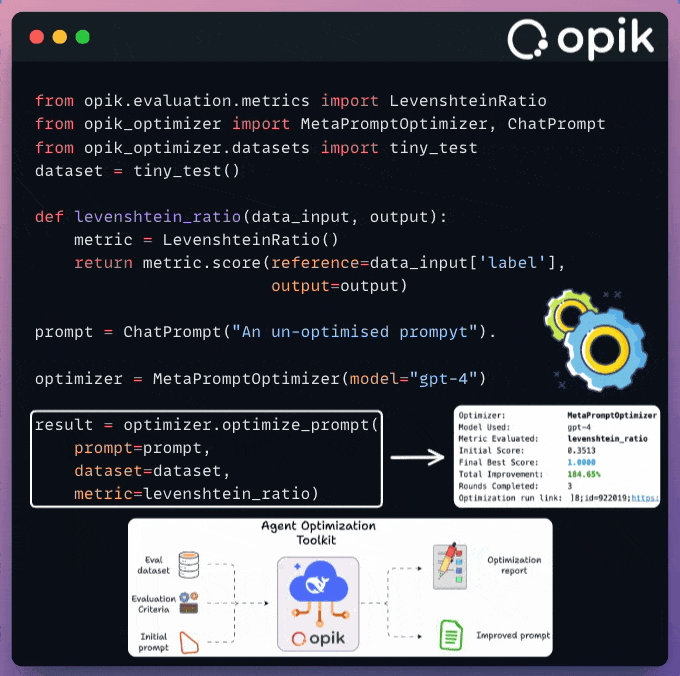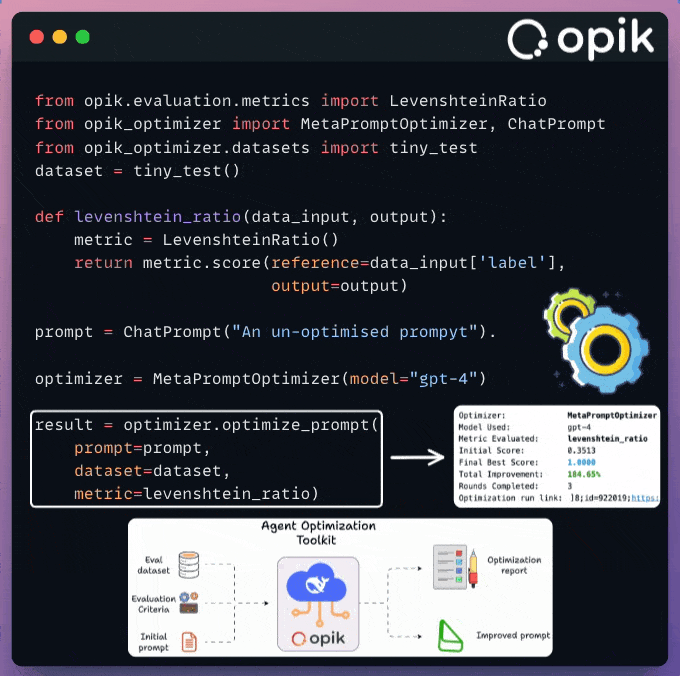
Build an automated Agent optimization workflow
Top AI Engineers never do manual prompt engineering!
Comet’s Opik implements an automated technique to find the best prompts for any agentic workflow you’re building.
This snippet explains it:
The idea is simple yet powerful:
Start with an initial prompt & eval dataset
Let the optimizer iteratively improve the prompt
Get the optimal prompt automatically!
And this is done using just a few lines of code, as shown in the image above.
Opik is a 100% open-source LLM evaluation platform.
It helps optimize LLM systems for better, faster, cheaper performance, from RAG chatbots to code assistants. Opik offers tracing, evaluations, and dashboards.
The best part is that everything can run 100% locally because you can use any local LLM to power your optimizers and evaluators.
You can learn more about Agent Optimization in the docs here →
Build a Context Retrieval Layer Across Apps and Databases
Imagine you have data that’s spread across several sources (Gmail, Drive, etc.).
How would you build a unified query engine over it?
Many devs still think context retrieval is a linear pipeline:
Chunk → Embed → Retrieve → Generate
This works great for simple demos, but production systems need something fundamentally different.
To understand better, consider this query:
“Compare our Q4 sales performance in the Chicago region against last year’s projections formulated in a meeting with stakeholders.”
This single query requires:
Sales data from your SQL database
Graph relationships (organizational hierarchy)
Vector search over projection reports
Time-based filtering (Q4 this year vs last year)
Permission checks (for user authorization)
No single embedding lookup can handle this complexity!
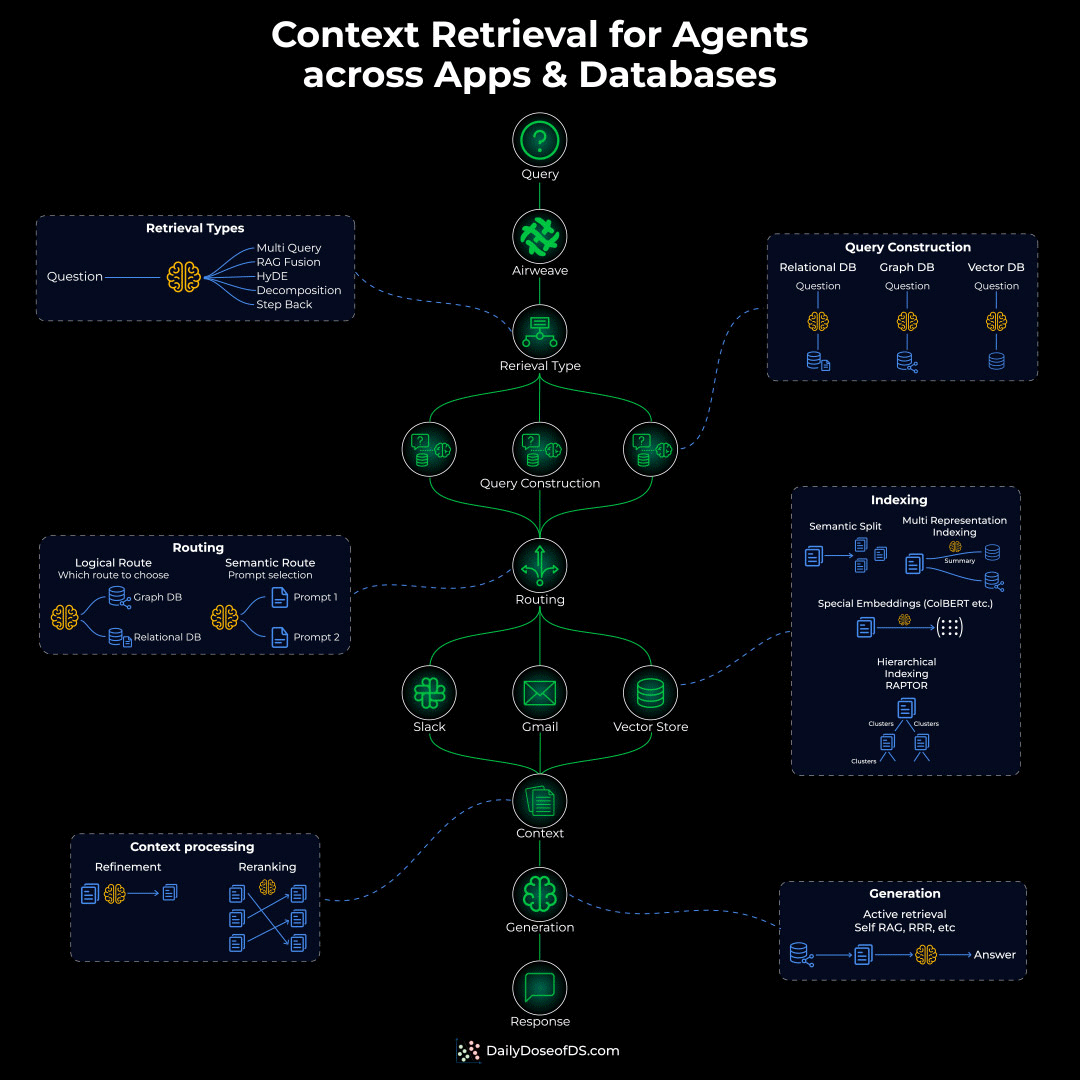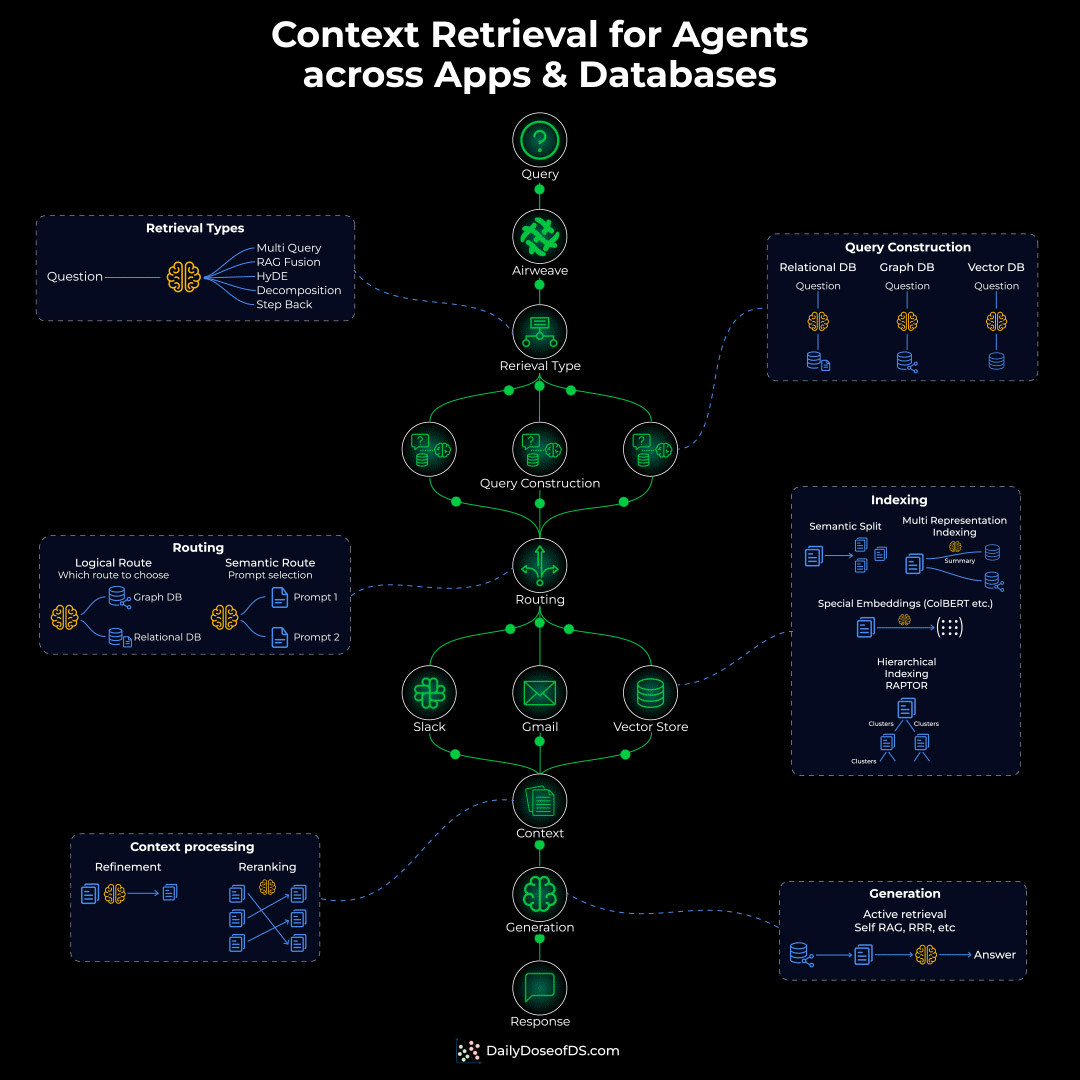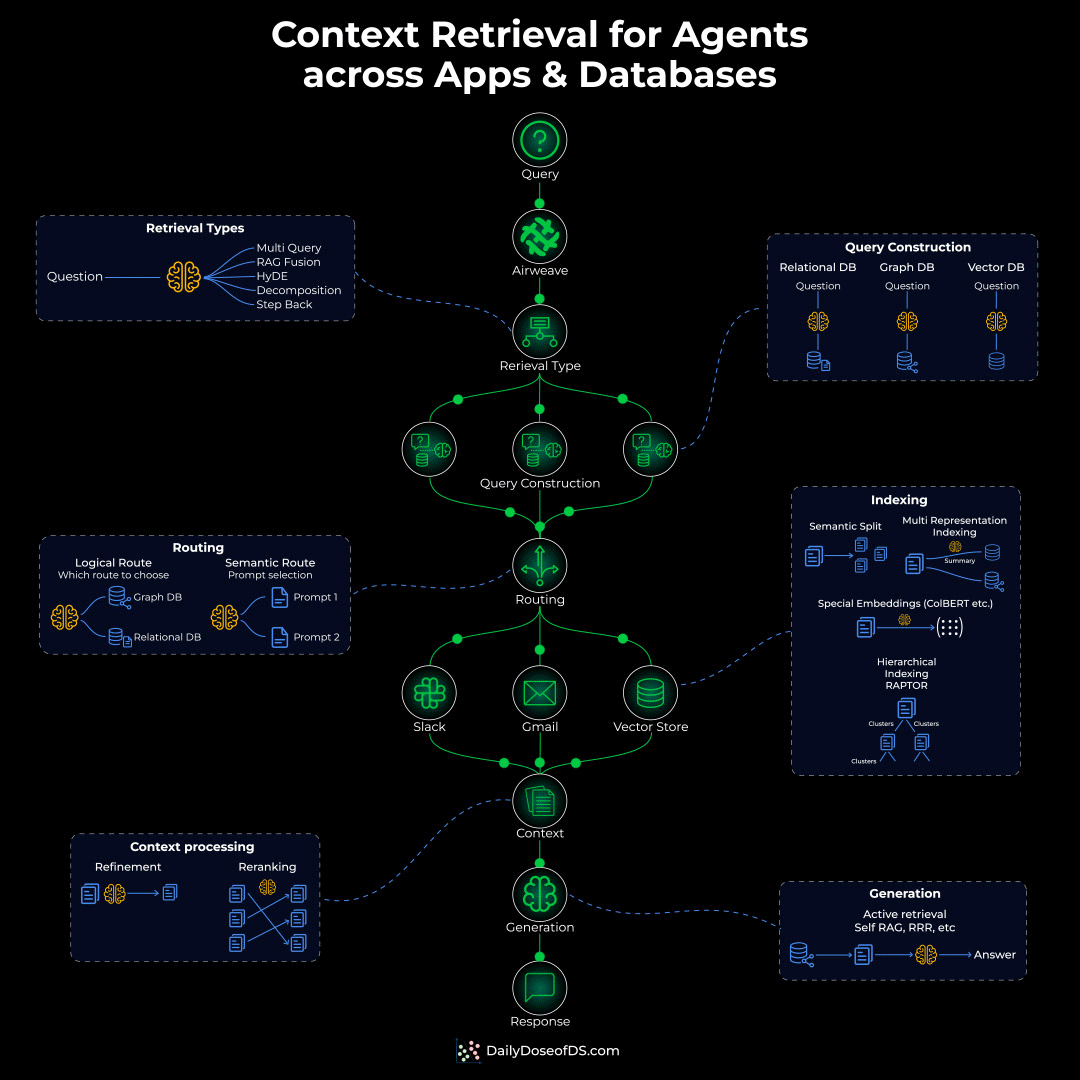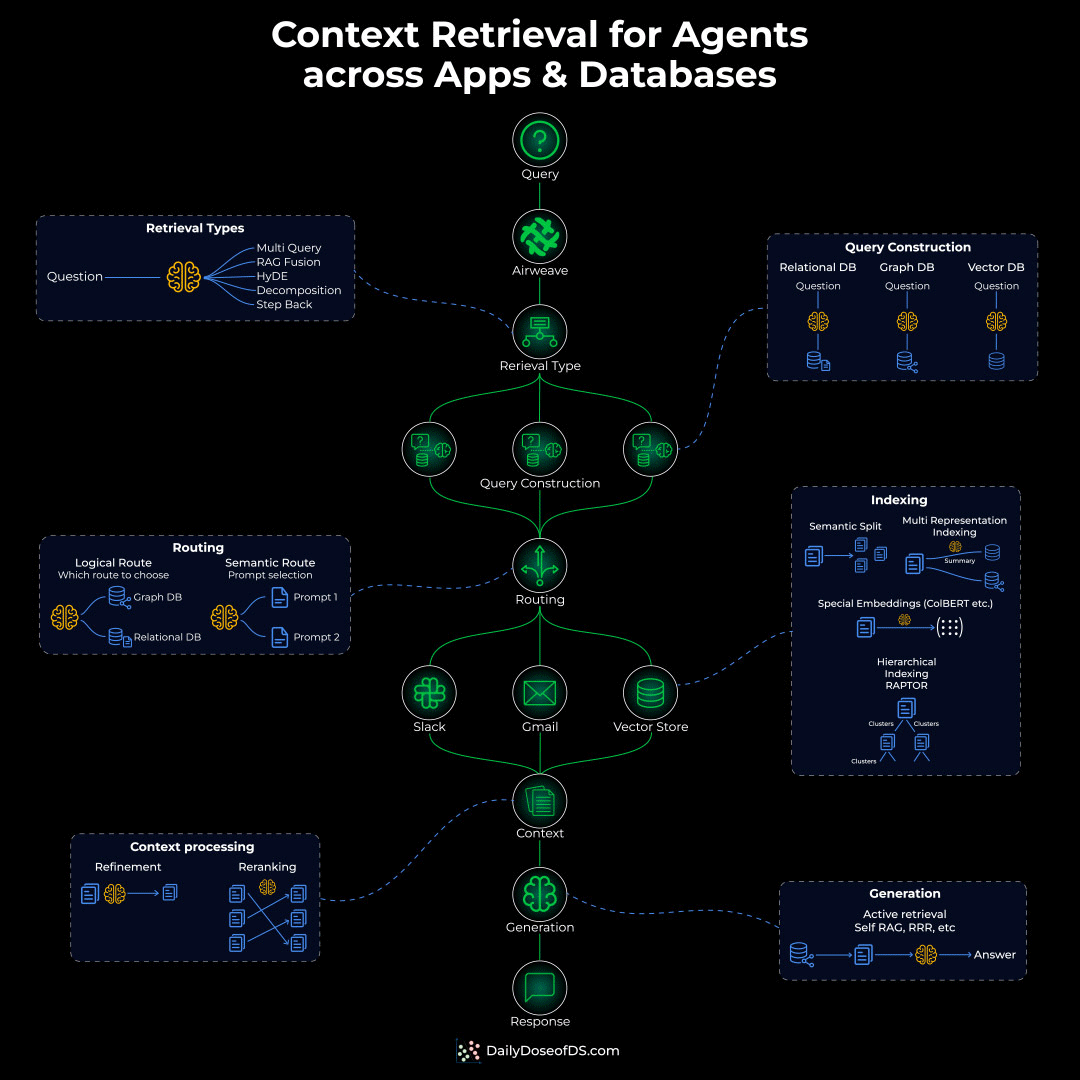
To actually solve this problem, you’d need to build an Agentic context retrieval system with five critical layers:
Indexing layer: Different content needs different indexing:
Semantic chunking for docs
Hierarchical indexing for nested content
Special indexing for sources like Calendar, Slack, etc.
Routing layer: Before retrieval, you need intelligent routing that decides:
Should the query hit a graph DB?
Does it need a structured SQL query?
Or semantic search for conceptual matching?
Query construction layer: The original query might need to be:
Decomposed into sub-queries
Translated into different query languages (SQL, Cypher, vector similarity)
Retrieval layer:
Apply permissions and access checks
Run multiple retrievals in parallel
Rerank based on relevance/recency
Generation layer: Synthesize a citation-backed response
That’s months of engineering before your first query hits production.
It’s definitely a tough problem to solve...
...but this is exactly how companies like Google (Vertex AI), Microsoft (Azure AI Search), and AWS (Amazon Q) have built their production agents.
If you want to see it in practice, this approach is actually implemented in Airweave, a recently trending 100% open-source framework that provides the context retrieval layer for AI agents across 40+ apps and databases.
It implements the entire production stack for context retrieval discussed above, like:
Source-specific indexing
Query expansion
Intelligent routing
Multi-source retrieval
Perplexity-like citation-backed response
Real-time sync to detect changes and optimally refresh the indexed data
For instance, to detect updates and initiate a re-sync, one might do timestamp comparisons.
But this does not tell if the content actually changed (maybe only the permission was updated), and you might still re-embed everything unnecessarily.
Airweave handles this by implementing source-specific hashing techniques like entity-level hashing, file content hashing, cursor-based syncing, etc.
You can see the full implementation on GitHub and try it yourself.
As a takeaway, remember that context retrieval for Agents is an infra problem, not an embedding problem.
You need to build for continuous sync, intelligent chunking, and hybrid search from day one.
You can find the Airweave repo here →
Some time back, we recorded a live demo, where you can learn how to provide agents with a context retrieval layer that can search across any app, database, or document store in real time.
It seamlessly connects to tools like Notion, Google Drive, and SQL databases, transforming their contents into searchable knowledge.
The entire setup runs locally inside a Docker container on your machine.
You can also expose it via an API and an MCP server.
GitHub repo → github.com/airweave-ai/airweave (don’t forget to star it)
👉 Over to you: How would you solve this problem?
Thanks for reading!