Context Engineering: Foundations, Categories, and Techniques of Prompt Engineering
The full LLMOps course (with code).
MongoDB Voyage-4: The First MoE Embedding Model in Production
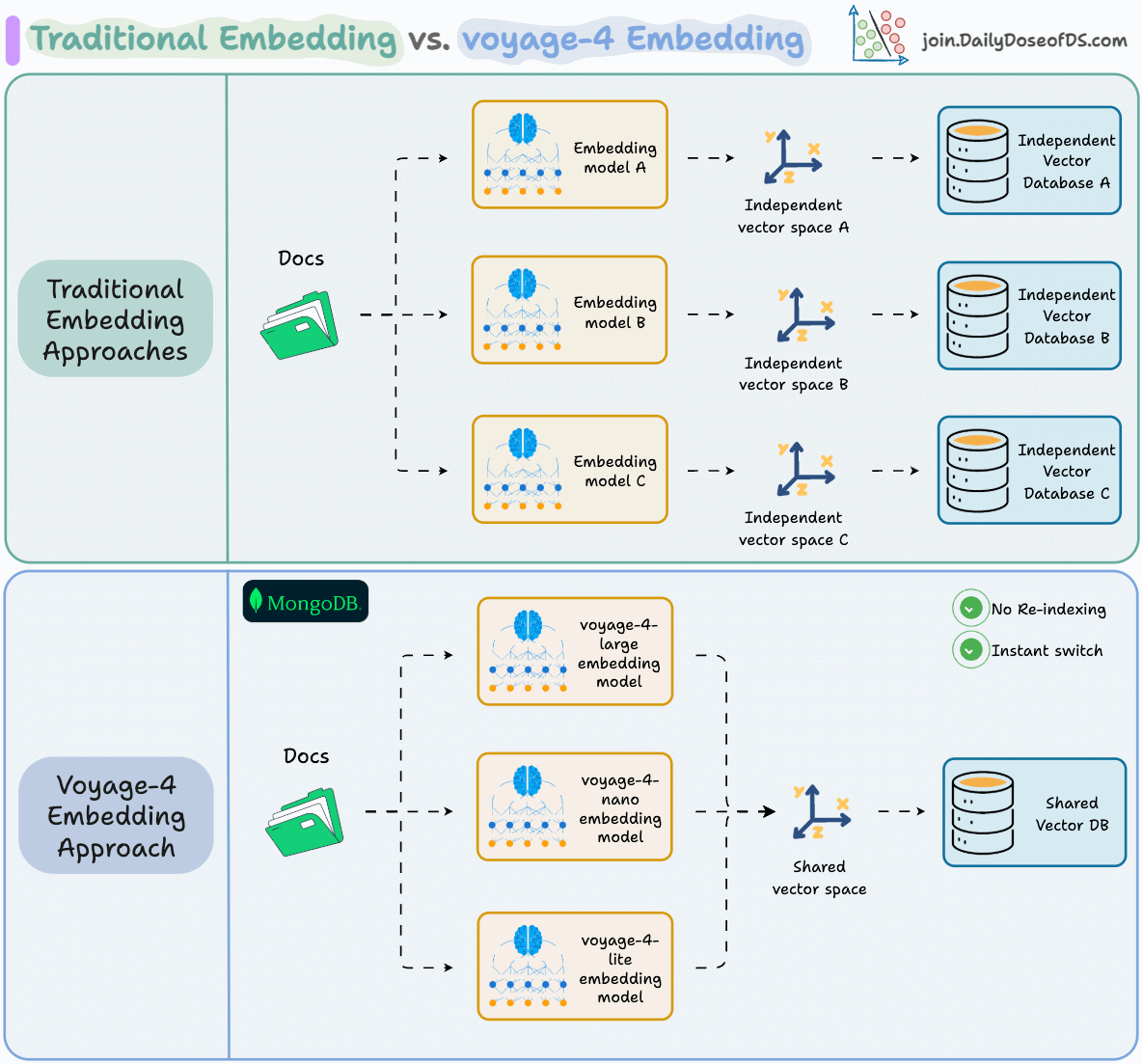
Switching embedding models shouldn’t require rebuilding your entire index.
But that’s exactly what happens with traditional embedding stacks. Each model produces vectors in its own latent space, so upgrading means re-embedding every document from scratch.
MongoDB’s voyage-4 series solves this with a shared vector space across the entire model family.
The workflow becomes simple: → Prototype locally with voyage-4-nano (open-weights on HuggingFace) → Deploy with voyage-4-large for production quality → No re-indexing required
voyage-4-large also uses a Mixture of Experts architecture, activating only relevant parameters per query, delivering state-of-the-art accuracy at 40% lower serving costs.
The model you start with should not lock you into how your system evolves.
You can download MongoDB’s voyage-4-nano model from HF here →
Thanks to MongoDB for partnering today!
Context Engineering: Foundations, Categories, and Techniques of Prompt Engineering
Part 5 of the full LLMOps course is now available, where we cover context (and prompt) engineering from a system perspective, while also learning about in-context learning, types of prompts, and prompting techniques.
It also covers hands-on code demos to understand prompt types and CoT implementation.
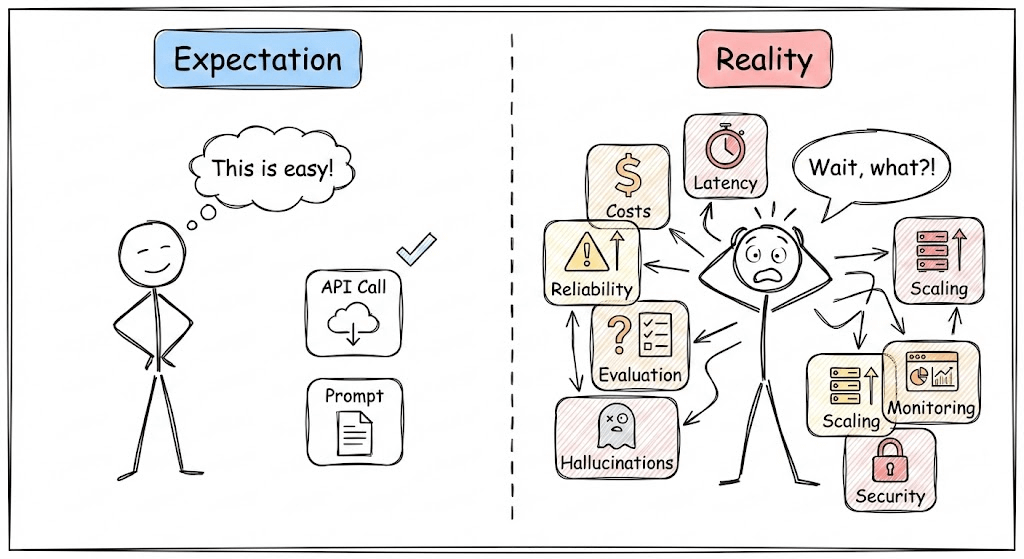
There’s a widening gap in the industry right now.
On one side: teams shipping impressive LLM demos in days. On the other: the same teams are struggling for months to make those demos production-ready.
The gap isn’t talent or resources.
It’s that production LLM systems require thinking most engineers haven’t developed yet, around costs, latency, reliability, and evaluation in a world where outputs are probabilistic and “correct” is subjective.
LLMOps bridges that gap.
It’s the discipline that takes you from “it works on my machine” to “it works at scale, under load, within budget, and without embarrassing failures.”
Through this course, we intend to help you build that production mindset systematically. Each chapter breaks down the concepts you need, backs them with clear examples and diagrams, and gives you hands-on implementations you can actually use.
More importantly, it develops the critical thinking to navigate decisions that have no single right answer, because in LLM systems, the tradeoffs are constant and the playbook is still being written.
Just like the MLOps course, each chapter will clearly explain necessary concepts, provide examples, diagrams, and implementations.
As we progress, we will see how we can develop the critical thinking required for taking our applications to the next stage and what exactly the framework should be for that.
👉 Over to you: What would you like to learn in the LLMOps course?
Thanks for reading!