Graph DBs vs. FalkorDB
...explained visually!
Graph databases have a problem that makes it difficult to scale AI applications in production.
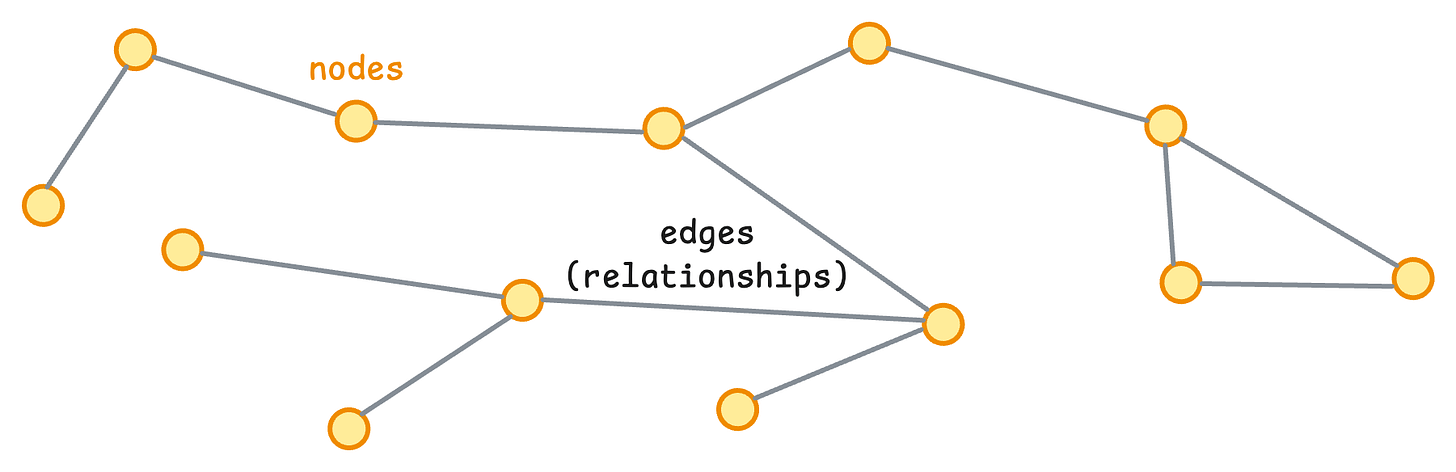
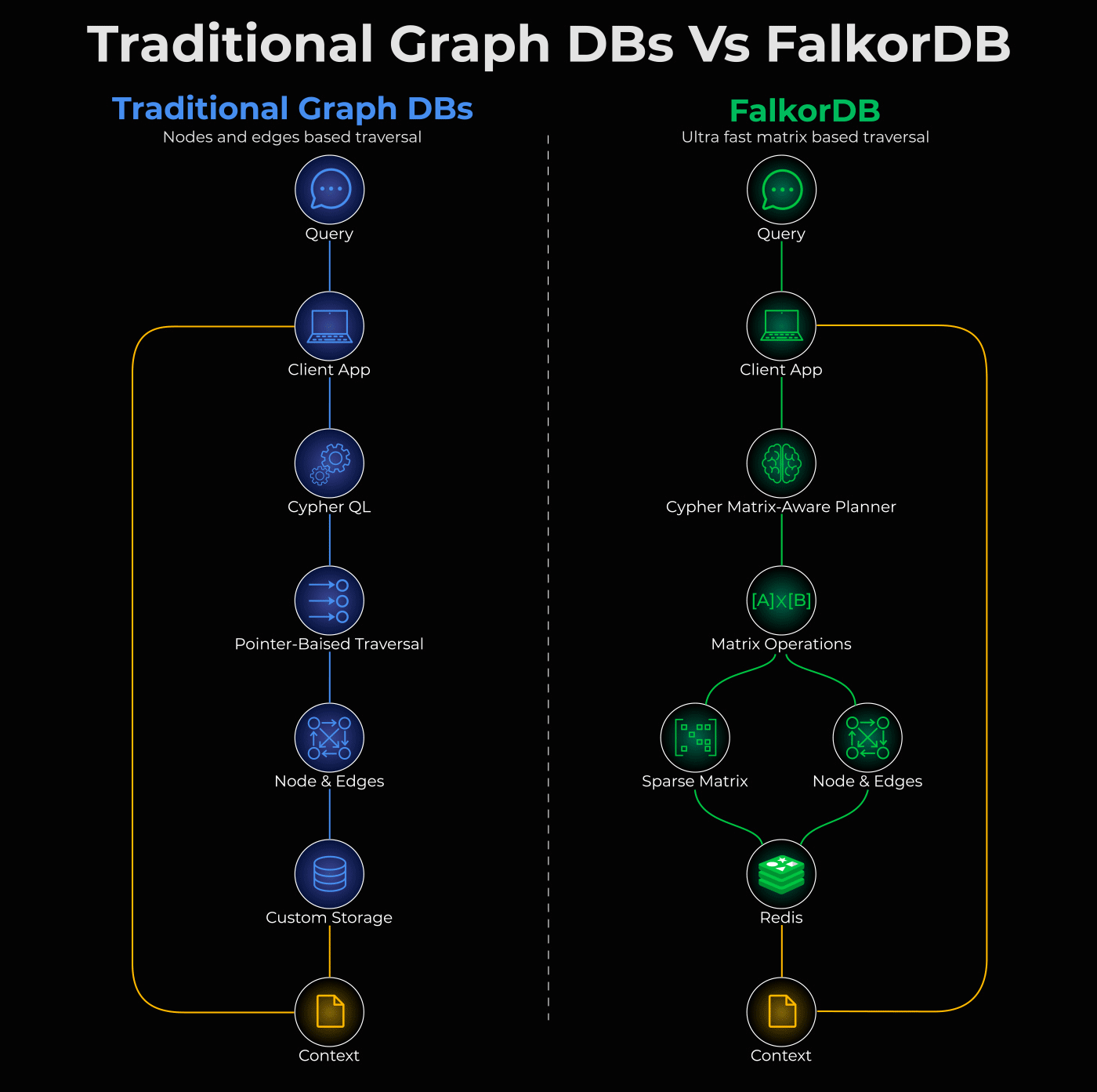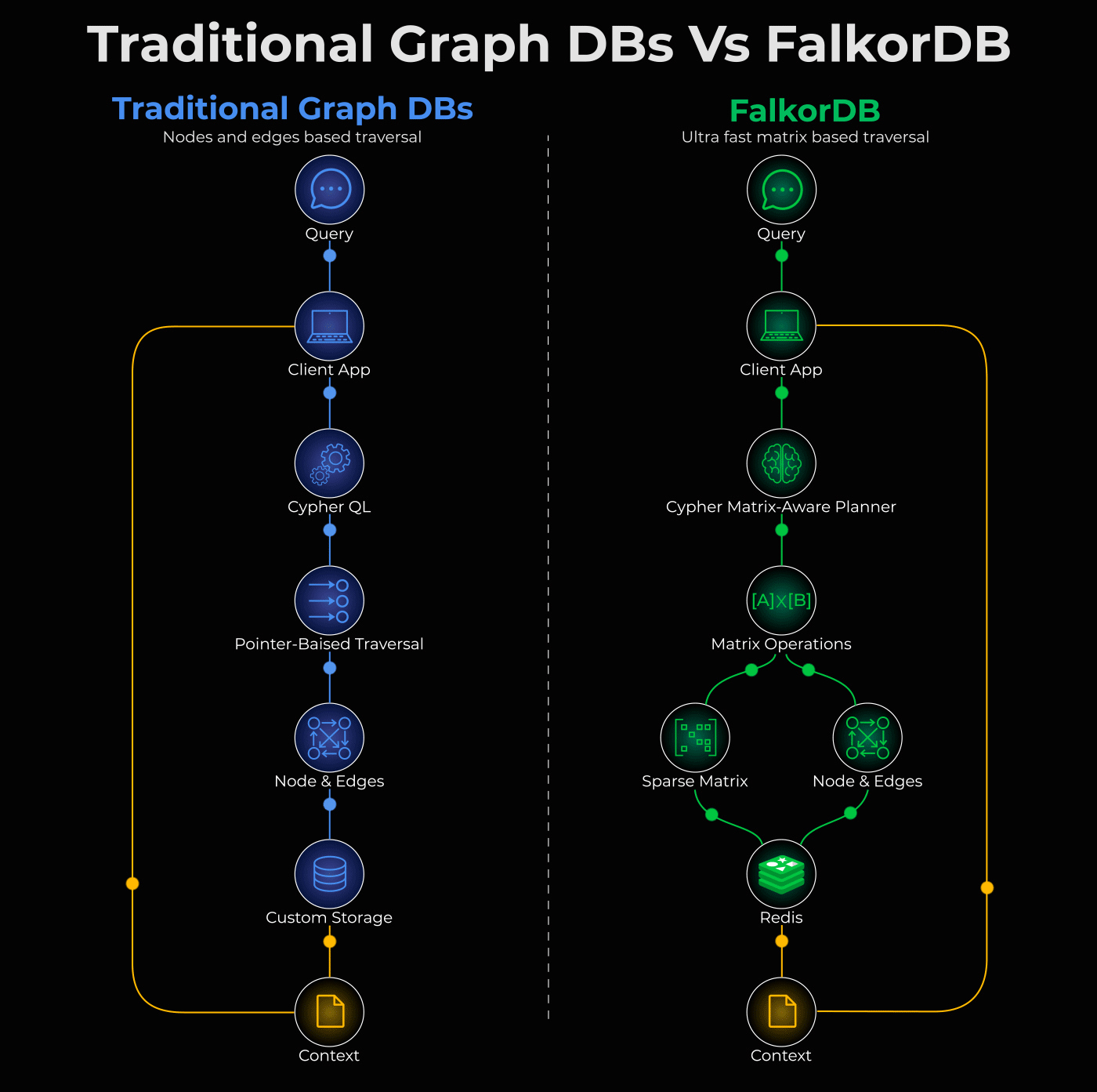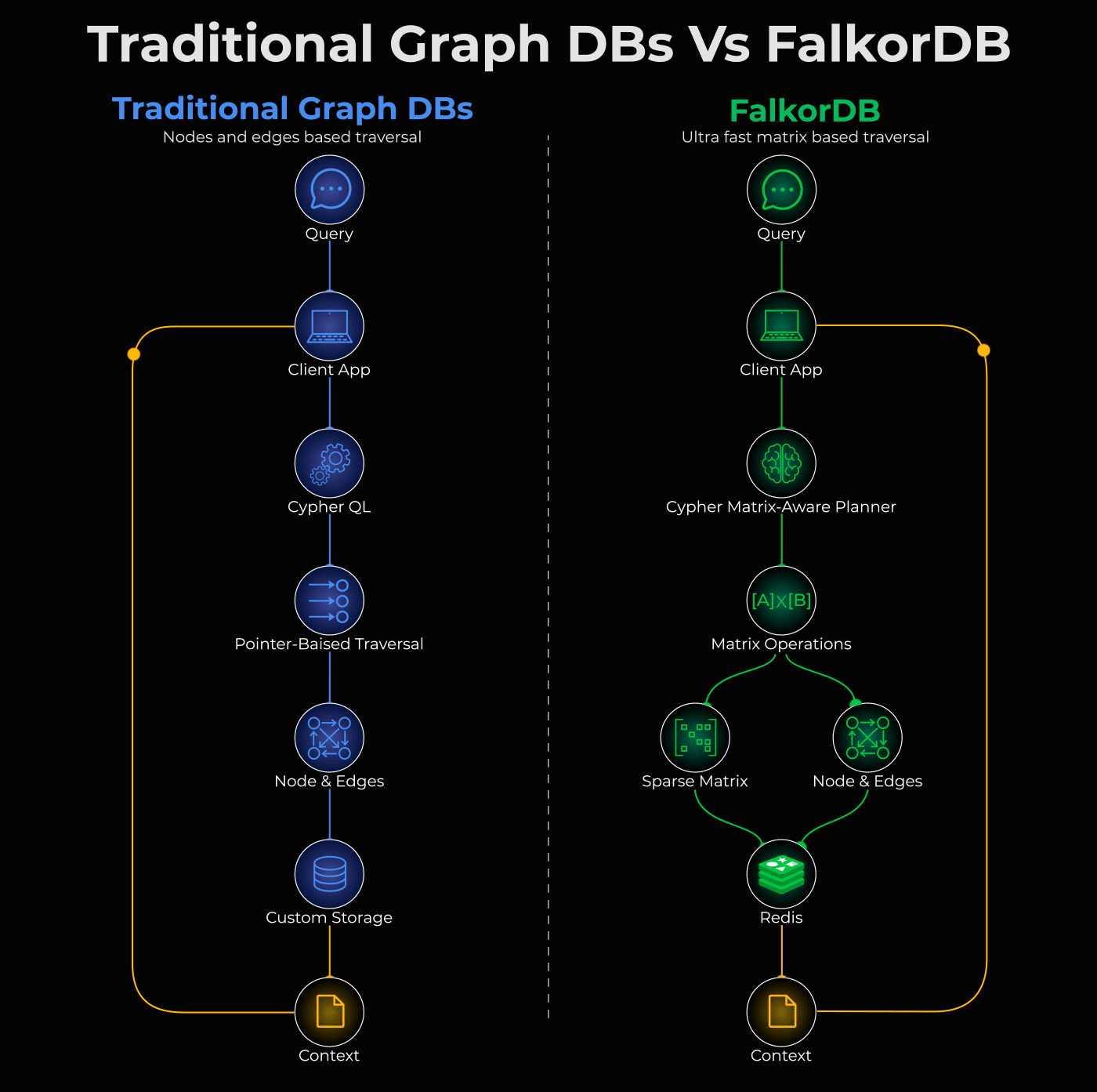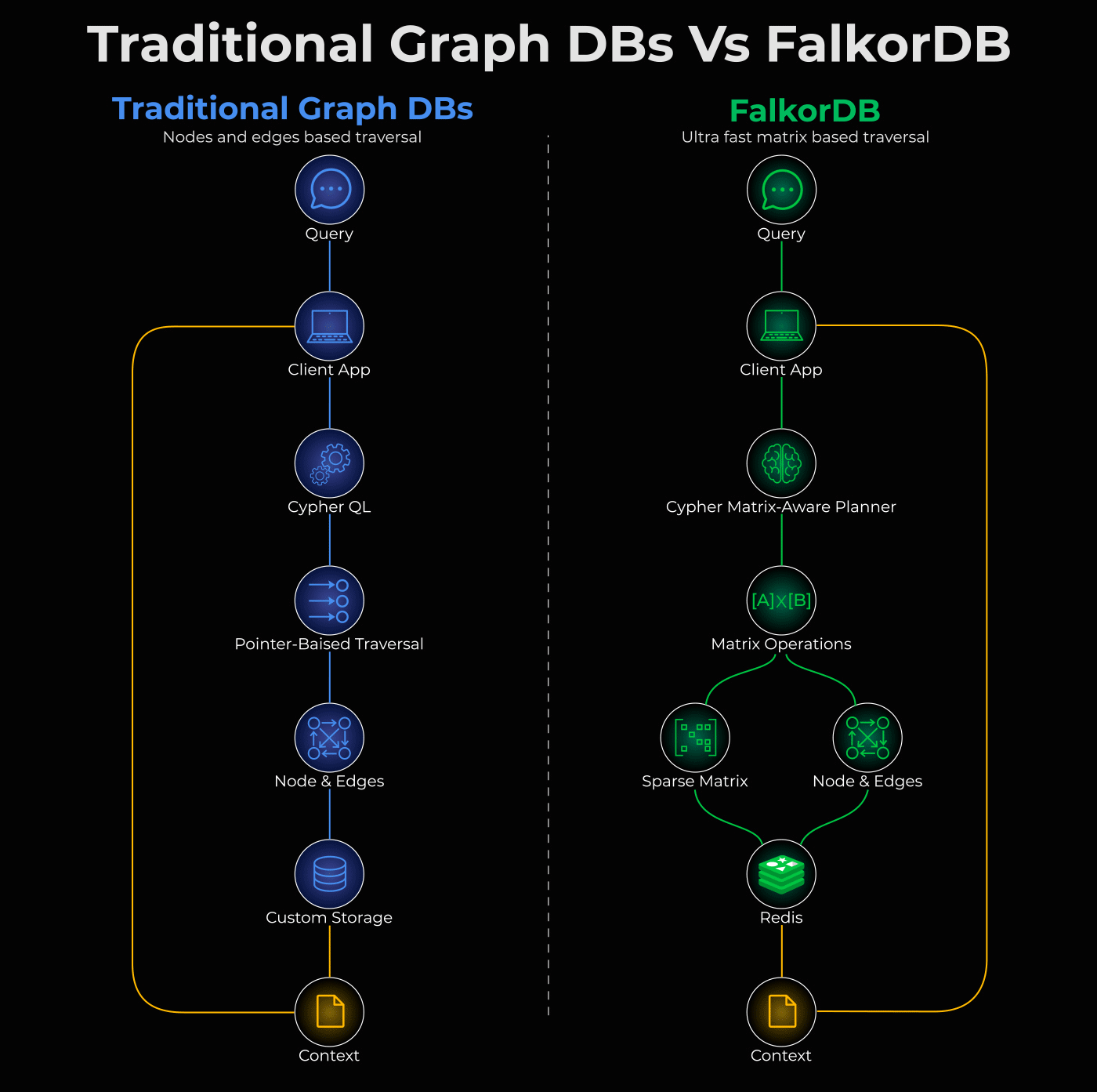
Essentially, a graph DB stores two things: nodes (entities) and edges (relationships between them).
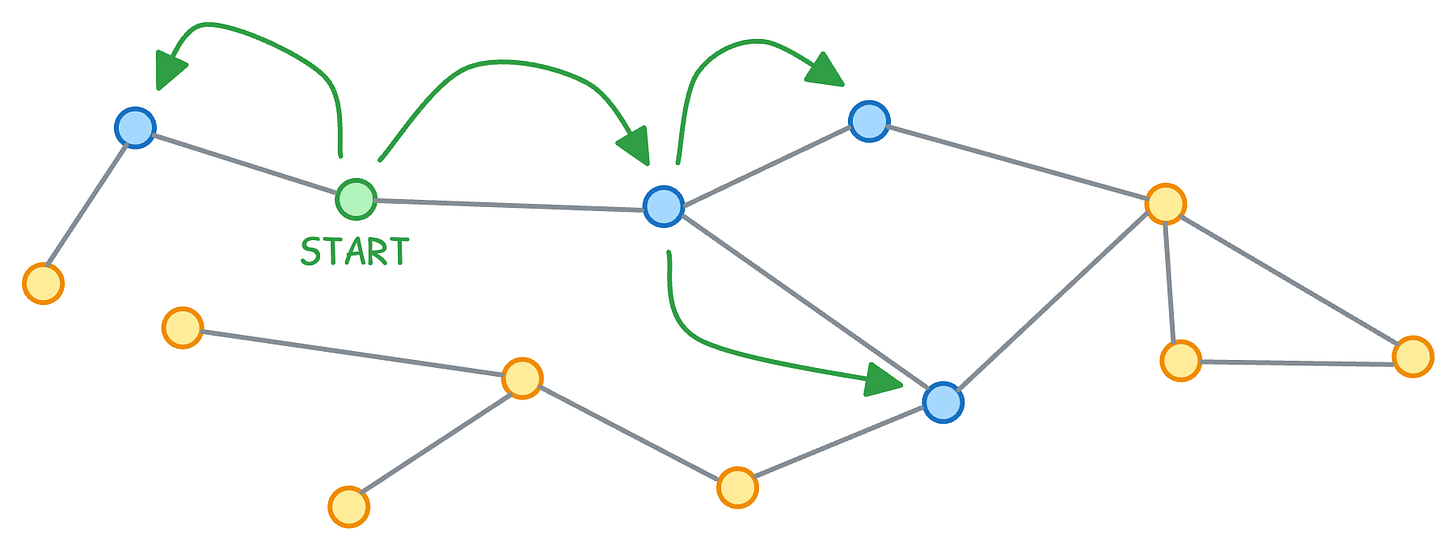
When you query a traditional graph DB, it traverses by “pointer chasing”:
Start at a node
Follow a pointer to the connected node
Follow another pointer
Repeat
This is inherently sequential. One hop at a time. And as your graph grows, this gets painfully slow.
FalkorDB (open-source) is taking a new approach to solve this and asks a different question: What if we represent the entire graph as a matrix?
Here’s how it works:
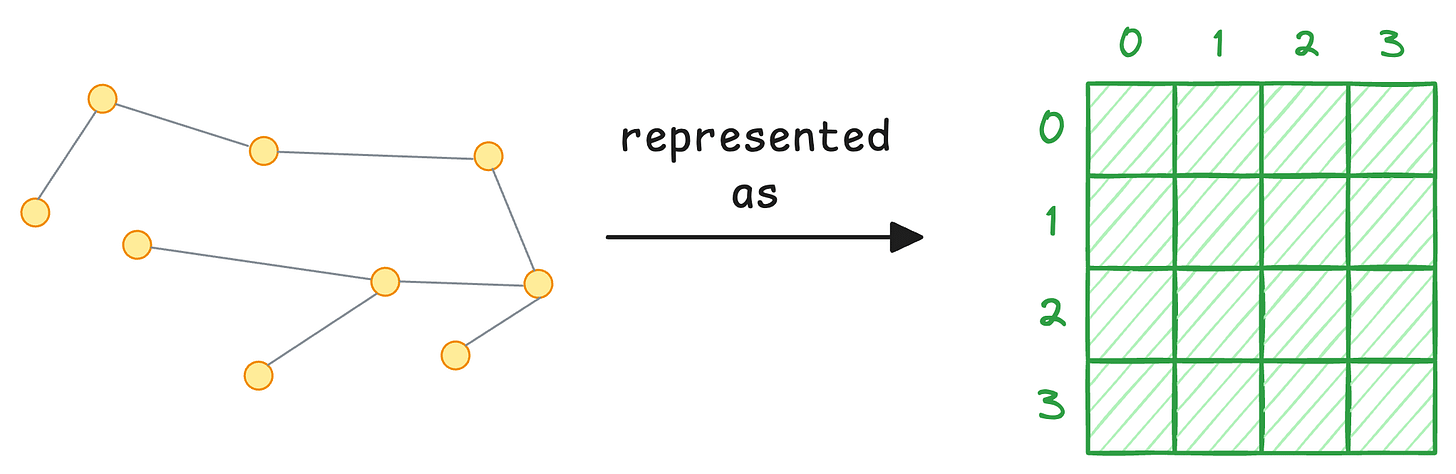
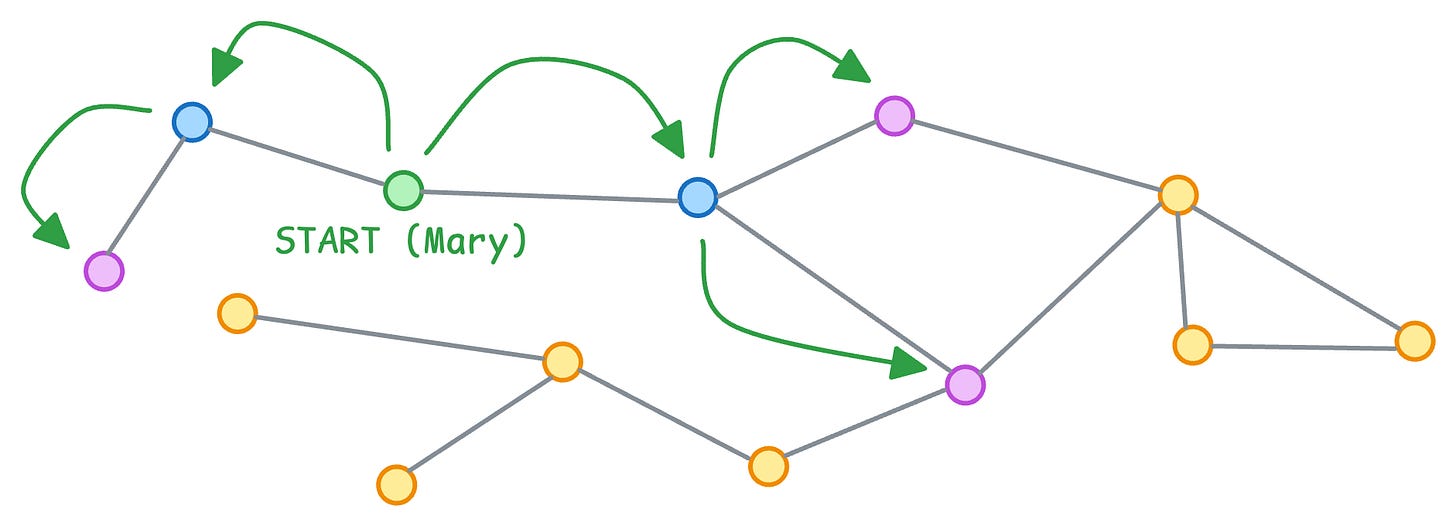
Imagine a simple grid. Rows are source nodes, columns are destination nodes.
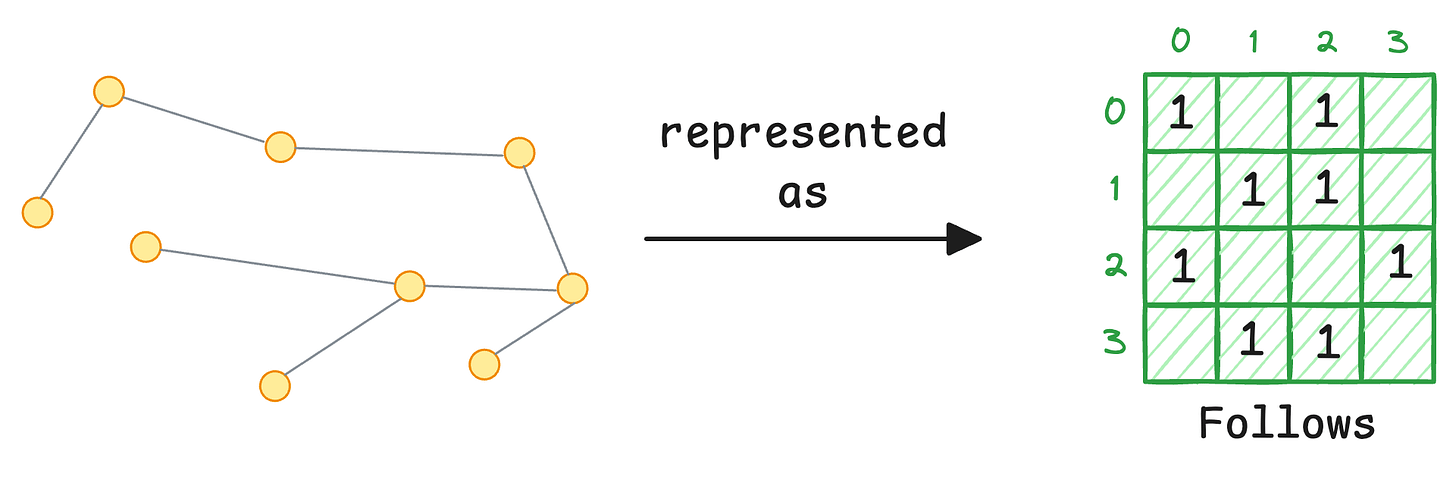
If Mary follows Bob, you set position [Mary, Bob] = 1.
That’s it. Your entire graph is now a matrix of 1s and 0s.
Let’s call this the Follows matrix (F).
Here’s where it gets interesting:
Finding who Mary’s friends follow? In a traditional graph DB, you hop twice: Mary (Green node) → friends (blue nodes) → friends’ friends (purple node).
But with matrices, you multiply the Follows matrix by itself: F × F = F² (you can actually verify this in practice with a dummy code).
This takes just one operation, and you’re done!
Similarly, a complex pattern like “A follows B, B likes C” becomes: Follows × Likes
This means you can represent traversal as math operations.
Why this matters:
Matrix operations have been optimized for 50+ years
Modern hardware (CPUs/GPUs) is built to crunch matrices
Operations run in parallel (pointer-chasing simply cannot)
While there are a few more optimizations involved (like using sparse matrices, etc.), this approach makes FalkorDB 496x faster than Neo4j.
The graphic below shows this difference clearly.
Traditional graph DBs go through Cypher QL → Pointer-Based Traversal,
FalkorDB uses a Matrix-Aware Planner that converts queries into matrix operations.
FalkorDB is 100% open source and built entirely on this principle:
Native Redis module (in-memory, ultra-fast)
Powered by GraphBLAS for sparse matrix operations
Auto-translates Cypher queries into matrix algebra
This is hugely important for AI applications because…
Modern AI agents and RAG systems need to traverse complex relationships in real-time. When an agent reasons through a knowledge graph to connect users to actions, every millisecond of latency compounds.
Vector DBs capture semantic similarity. But they miss explicit relationships.
Knowledge graphs fill that gap.
And when your agent needs to perform multi-hop reasoning across thousands of connected entities, matrix-based traversal makes it easier to scale your AI application without running into latency bottlenecks.
FalkorDB is 100% open-source.
You can find the FalkorDB GitHub repo here →
We are working on a hands-on demo on this and will share that soon in this newsletter.
Thanks for reading!