How are QQ Plots Created?
Creating one from scratch.
In today’s newsletter:
The identity problem no one’s solving for AI Agents.
Now you can train LLMs in VS Code for free!
How are QQ Plots created?
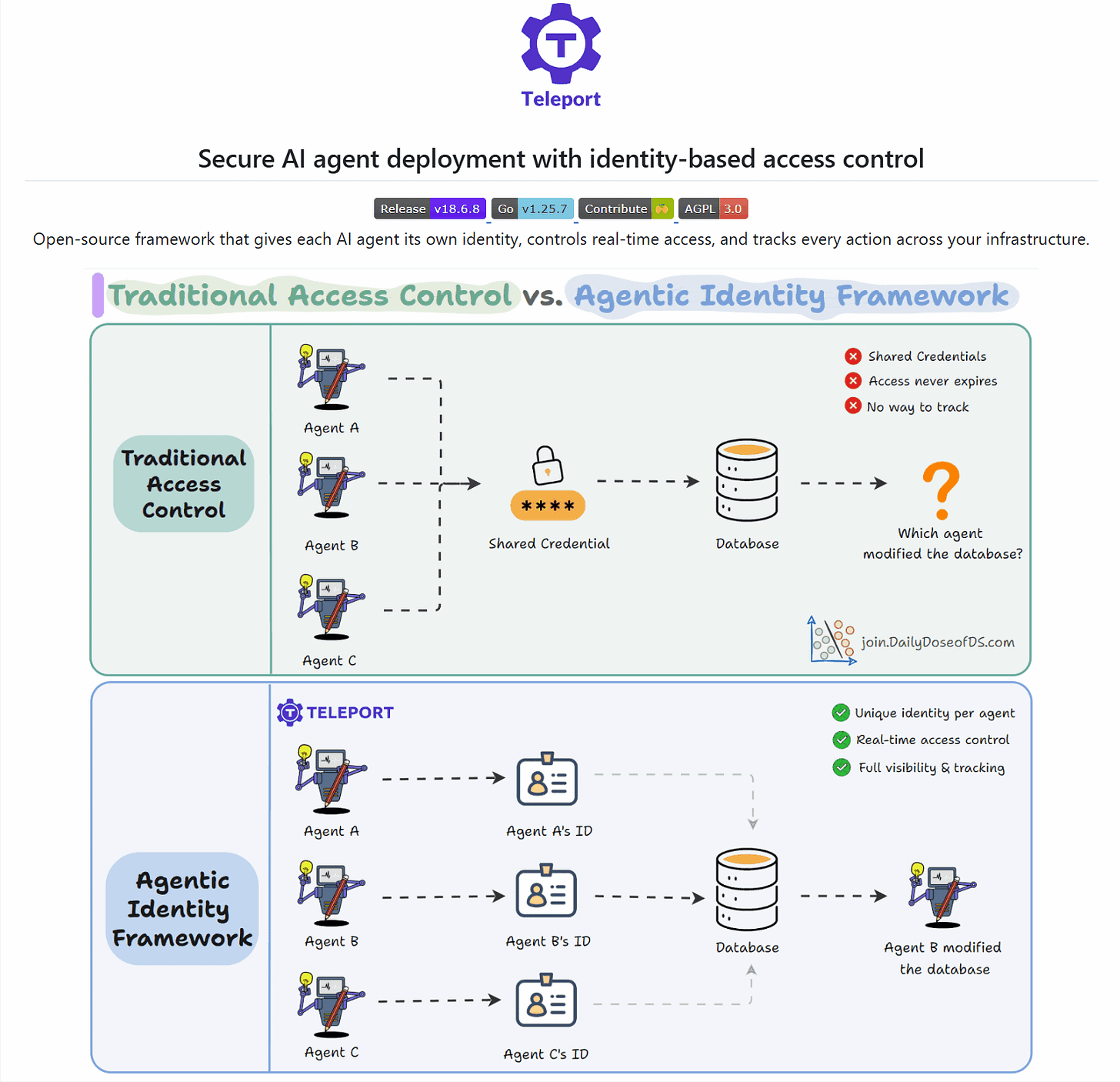
The identity problem no one’s solving for AI Agents
AI agents don’t have a security problem.
They have an identity problem.
Say you’ve deployed 47 agent workflows across your infrastructure.
At 3am, an agent modifies a production database. When you check your logs, you’ll notice that 47 agents had access. They all used the same service account, so you can’t tell which one did it.
IBM’s 2025 breach report found that 97% of organizations with AI-related breaches lacked proper AI access controls.
This happens because traditional security was built around human behavior: request access, get approved, complete the task, log out.
Agents don’t work that way.
They run continuously for hours or days, making independent decisions at machine speed. They don’t log out. They don’t pause between tasks. They just keep acting.
Microsoft projects 1.3 billion agents in enterprises by 2028. Most will inherit long-lived API tokens and overprivileged service accounts.
The fix isn’t better credentials. It’s giving every agent its own identity.
Teleport is building an open-source framework for exactly this. Here’s how it works:
Each agent gets its own cryptographic identity. No shared accounts, no static keys.
Access decisions happen in real-time, scoped to what the agent needs right now.
Every action traces back to a specific agent. Rogue behavior is detectable.
Agents connect to databases and tools through the framework, not through scattered credentials.
Deploy agents safely. See exactly what each one does.
The framework is open source. Check out the GitHub repo here →
More info on the framework here as well →
Thanks to Teleport for partnering with us today!
Now you can train LLMs in VS Code for free!
This guide by Unsloth shows you how to connect any fine-tuning notebook in VS Code to a Colab runtime.
Train locally or on a free Google Colab GPU.
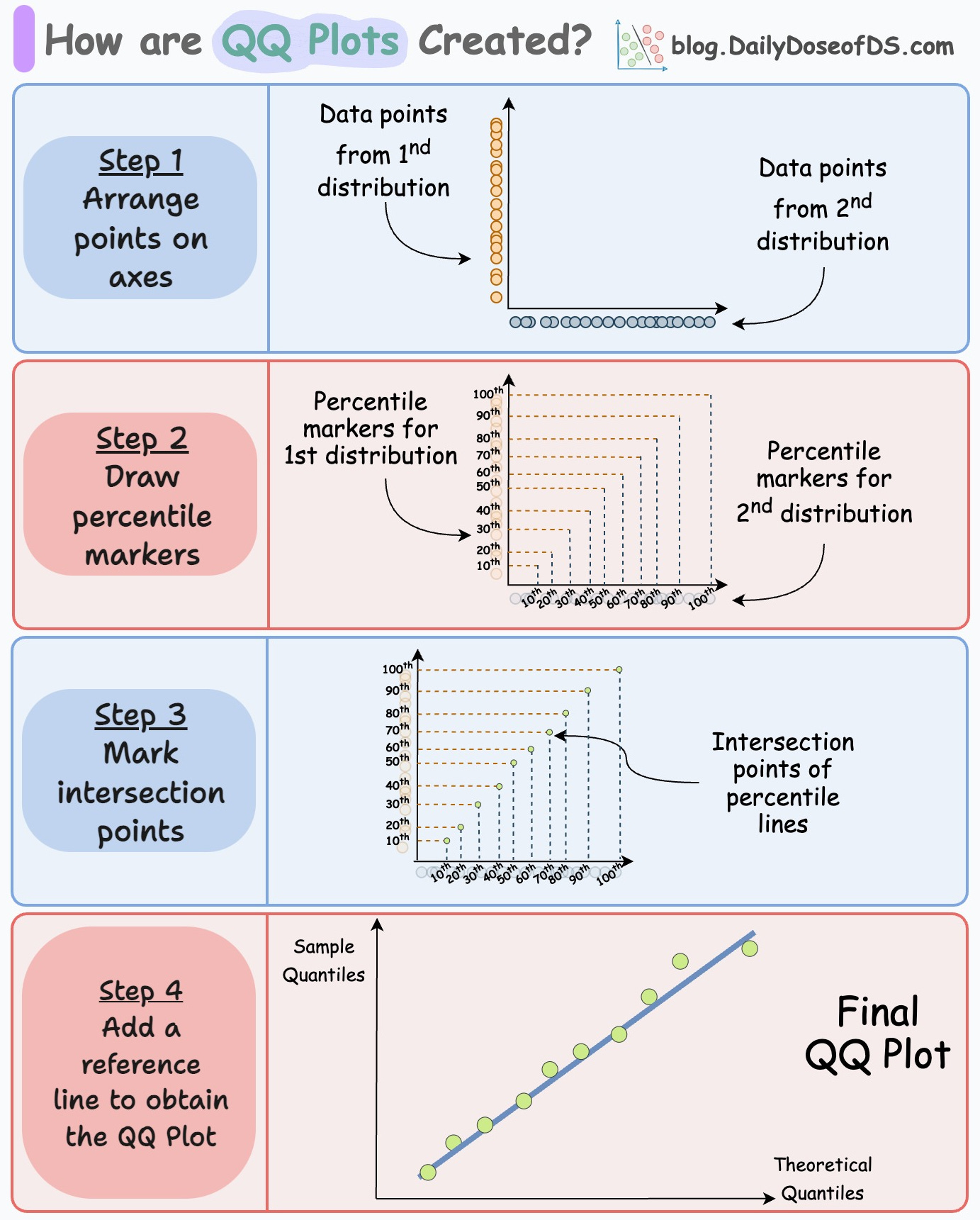
How are QQ Plots created?
A QQ plot lets you visually assess the similarity between two distributions:
By plotting the quantiles of the two distributions against each other, we can look at the deviations from the straight line to determine the differences between the two distributions.
But how is it created?
Let’s understand today!
The following visual depicts this process:
Consider two distributions—D1 and D2.
Step 1) Arrange points on axes:
Arrange points of D1 on the y-axis and D2 on the x-axis.
Step 2) Draw percentile lines
Create some percentile lines for both distributions.
For instance, mark the points of 10th percentile, 20th percentile, 30th percentile, etc. Once marked, intersect the corresponding lines:
Match the 10th percentile of D1 with 10th percentile of D2.
Match the 20th percentile of D1 with 20th percentile of D2.
and so on.
The intersection points gives us the points in a QQ plot:
Now, remove the percentile marker lines.
In a gist, the above plot depicts the location where the corresponding percentiles of the two distributions match.
Step 3) Add the reference line
Finally, add a reference line to determine the deviations between the two distributions. There are many ways to do this:
Draw a line connecting the 25th and 75th percentiles of both distributions.
Or, create a regression fit on the above scatter plot.
Typically, option #1 is preferred since a regression fit can be influenced by outliers.
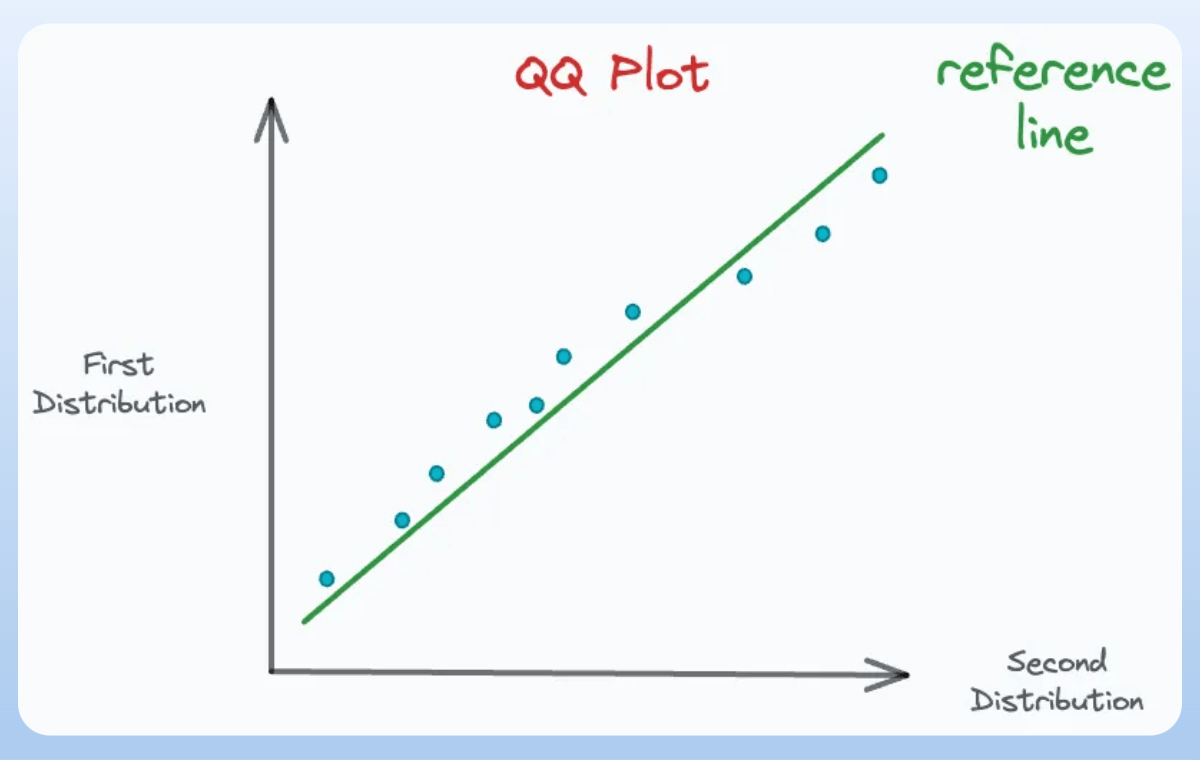
Adding the reference lines gives this QQ plot:
The deviations from this reference line mean that the corresponding percentiles do not align, which is an indicator of dissimilarity:
And the more percentiles we plot, the more accurate the QQ plot we get.
There are many applications of the QQ plot.
Imagine we want to determine if a distribution resembles a normal distribution. We can use a QQ plot for this.
D1: The observed distribution
D2: Normal distribution.
The closer the percentile points are to the reference line, the more the observed distribution matches a normal distribution:
👉 Over to you: What other plots do you typically struggle with and want me to cover?
Thanks for reading!
P.S. For those wanting to develop “Industry ML” expertise:
At the end of the day, all businesses care about impact. That’s it!
Can you reduce costs?
Drive revenue?
Can you scale ML models?
Predict trends before they happen?
We have discussed several other topics (with implementations) that align with such topics.
Here are some of them:
Learn everything about MCPs in this crash course with 9 parts →
Learn how to build Agentic systems in a crash course with 14 parts.
Learn how to build real-world RAG apps and evaluate and scale them in this crash course.
Learn sophisticated graph architectures and how to train them on graph data.
So many real-world NLP systems rely on pairwise context scoring. Learn scalable approaches here.
Learn how to run large models on small devices using Quantization techniques.
Learn how to generate prediction intervals or sets with strong statistical guarantees for increasing trust using Conformal Predictions.
Learn how to identify causal relationships and answer business questions using causal inference in this crash course.
Learn how to scale and implement ML model training in this practical guide.
Learn techniques to reliably test new models in production.
Learn how to build privacy-first ML systems using Federated Learning.
Learn 6 techniques with implementation to compress ML models.
All these resources will help you cultivate key skills that businesses and companies care about the most.