Manual RAG Pipeline vs Unified Knowledge Bases
...explained visually.
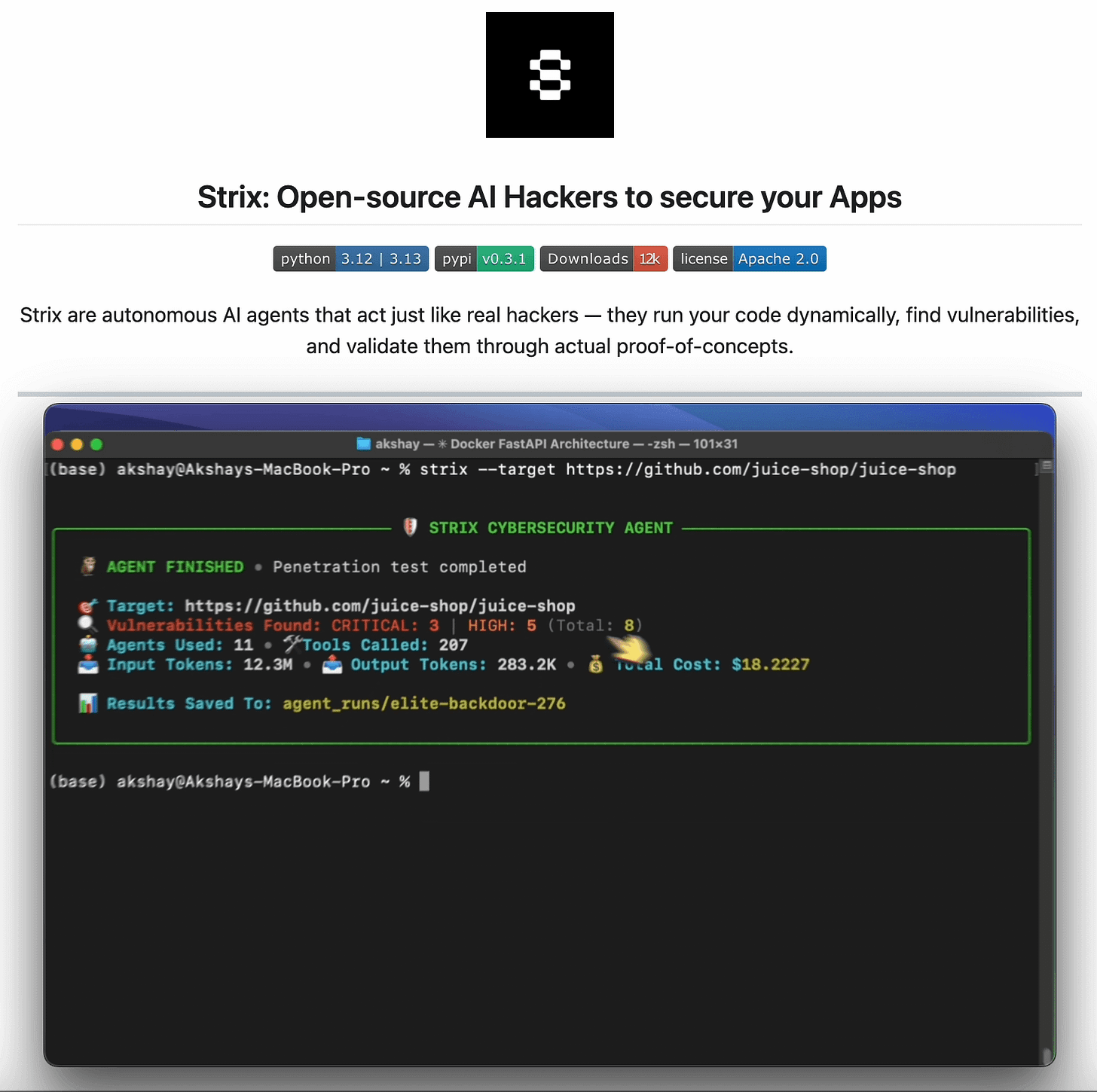
Agent hackers to test your AI apps (open-source)!
Pentesting firms don’t want you to see this.
An open-source AI agent just replicated their $50k service.
A “normal” pentest today looks like this:
$20k-$50k per engagement
4-6 weeks of scoping, NDAs, kickoff calls
A big PDF that’s outdated the moment you ship a new feature
Meanwhile, AI agents are quietly starting to perform on par with human pentesters on the stuff that actually matters day-to-day:
Enumerating attack surface
Fuzzing endpoints
Chaining simple vulns into real impact
Producing PoCs and remediation steps developers can actually use
And they do it in hours instead of weeks and at a fraction of the cost.
This approach is actually implemented in Strix, a recently trending open-source framework (17k+ stars) for AI pentesting agent.
The framework spins up a team of AI “attackers” that probe your web apps, APIs, and code.
It then returns validated findings with exploit evidence, remediation steps, and a full PDF report that looks exactly like what you’d get from a traditional firm, but without a $50k invoice and a month-long wait time.
You can see the full implementation on GitHub and try it yourself.
Just run: strix --target https: //your-app .com and you are good to go.
Human red teams aren’t disappearing, but the routine pentest (pre-launch, post-refactor, quarterly checks) is clearly shifting to AI.
Strix is one of the first tools that makes that shift feel real instead of hypothetical.
You can find the GitHub repo here → (don’t forget to star it)
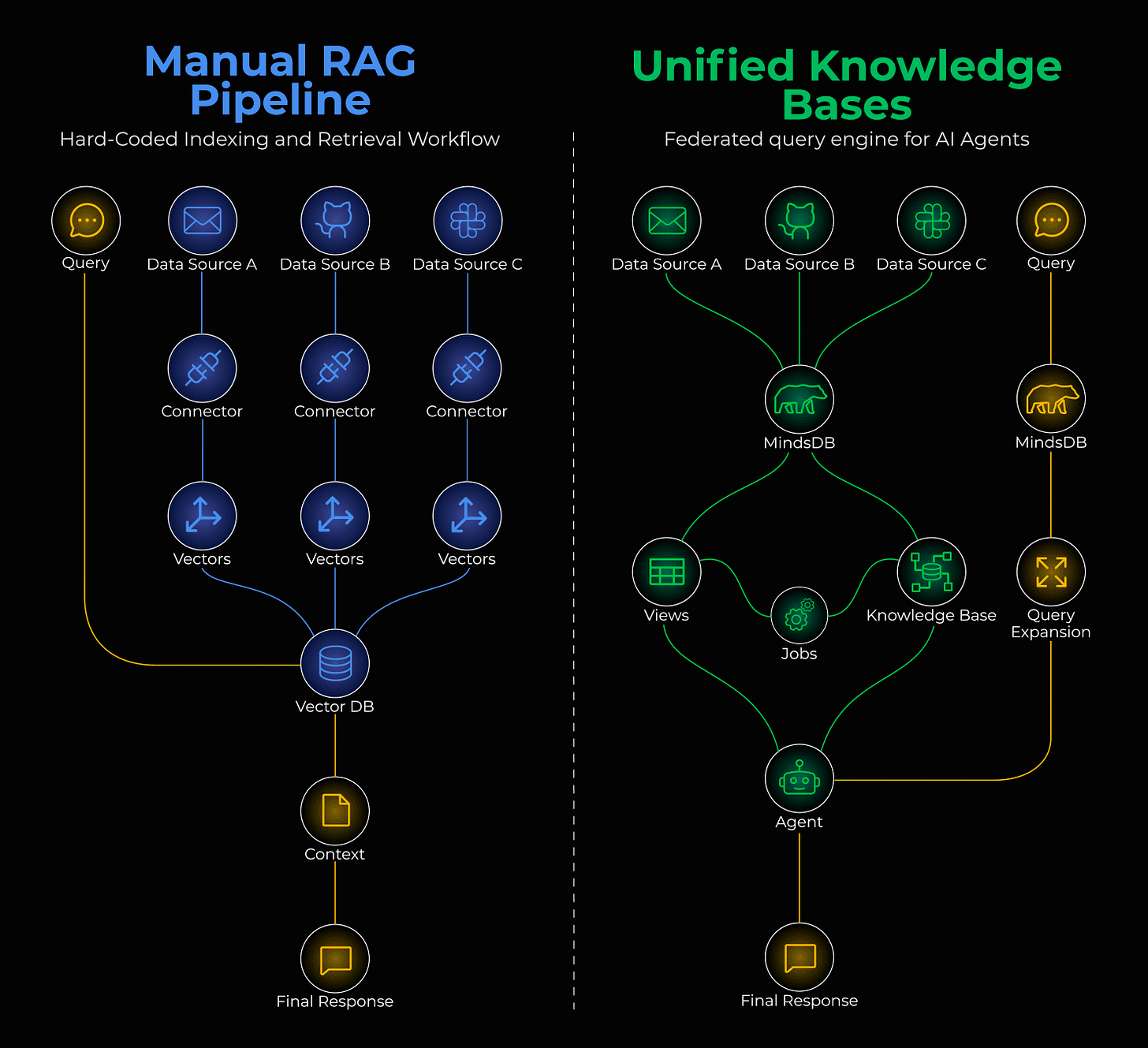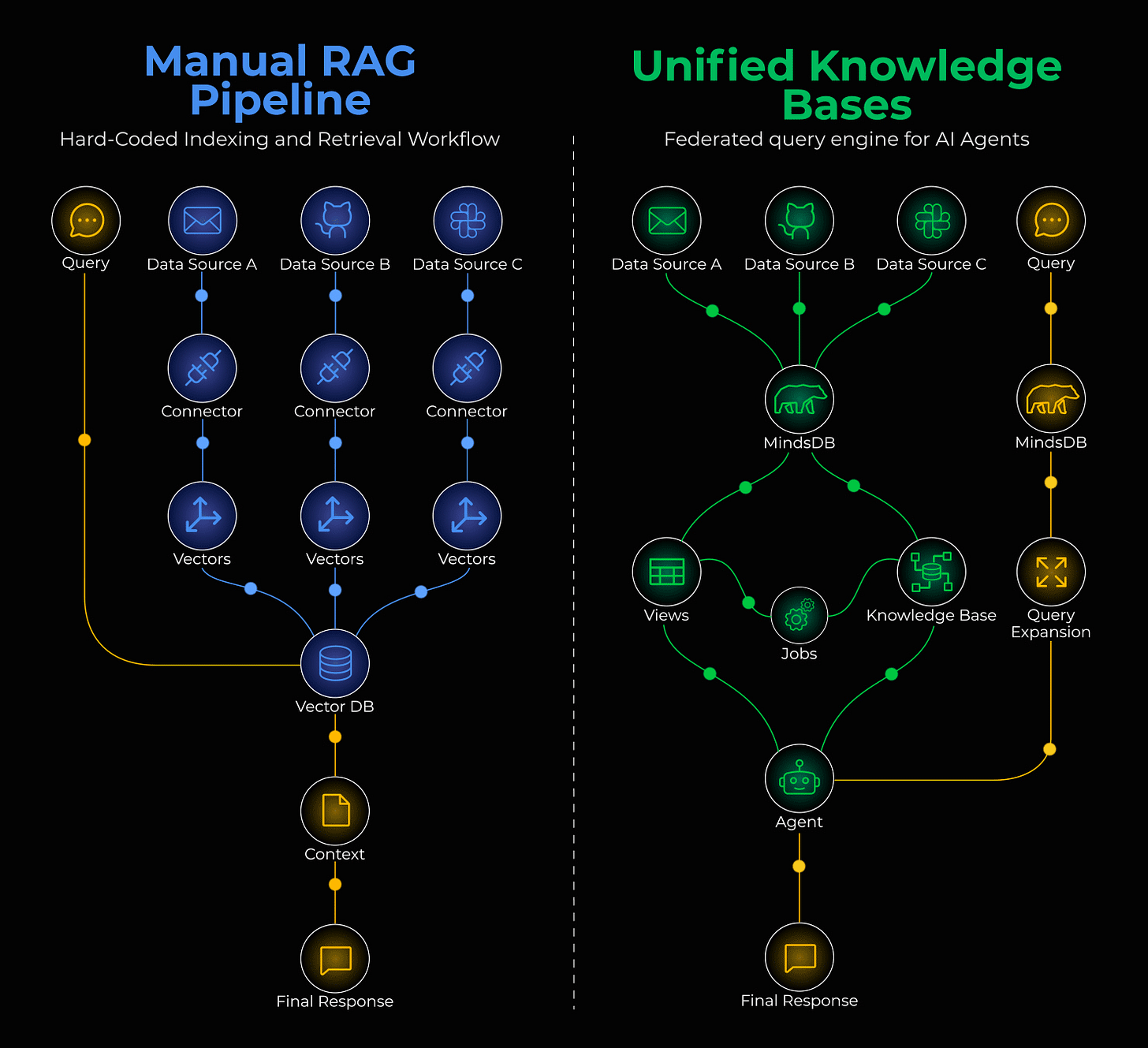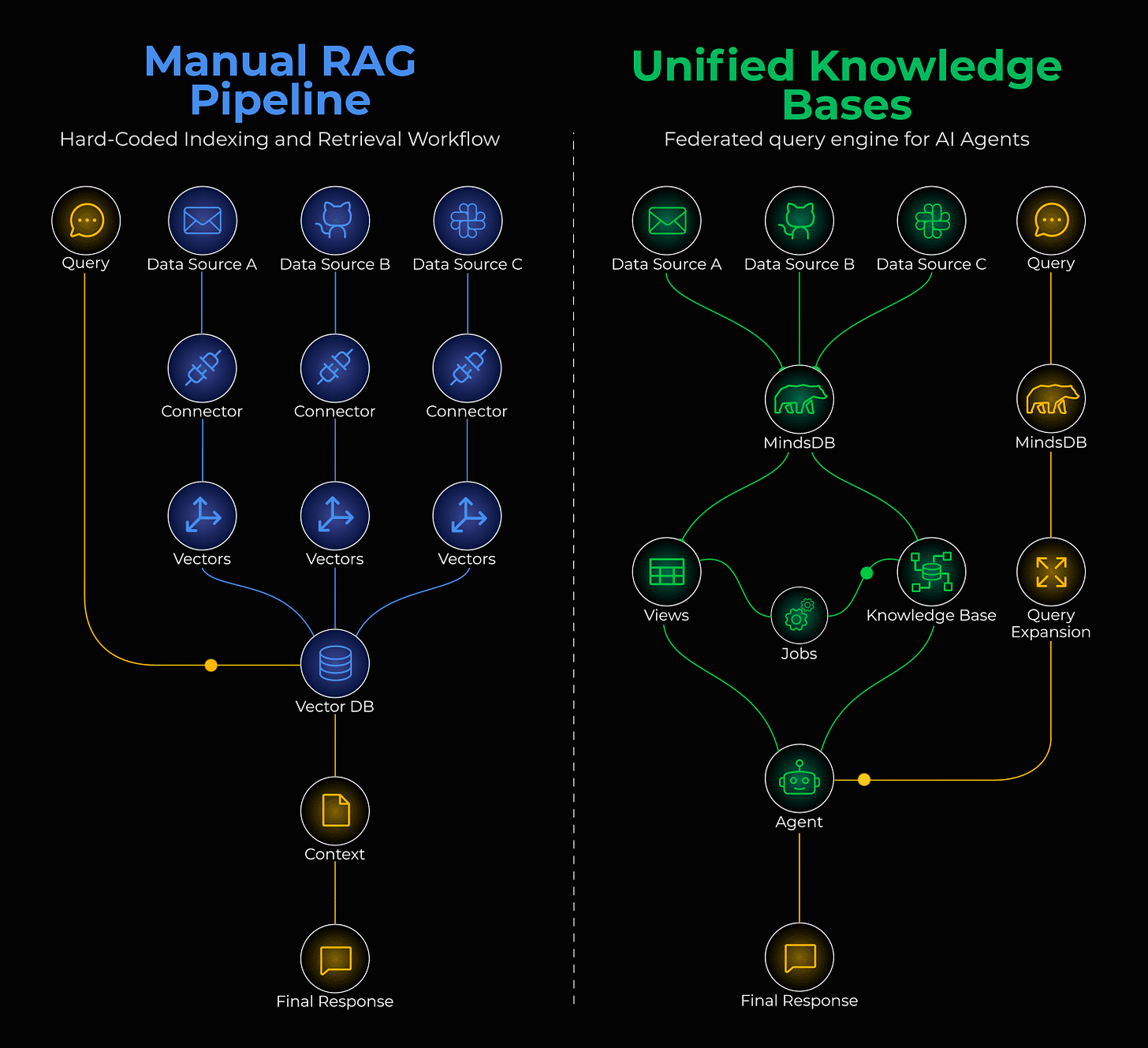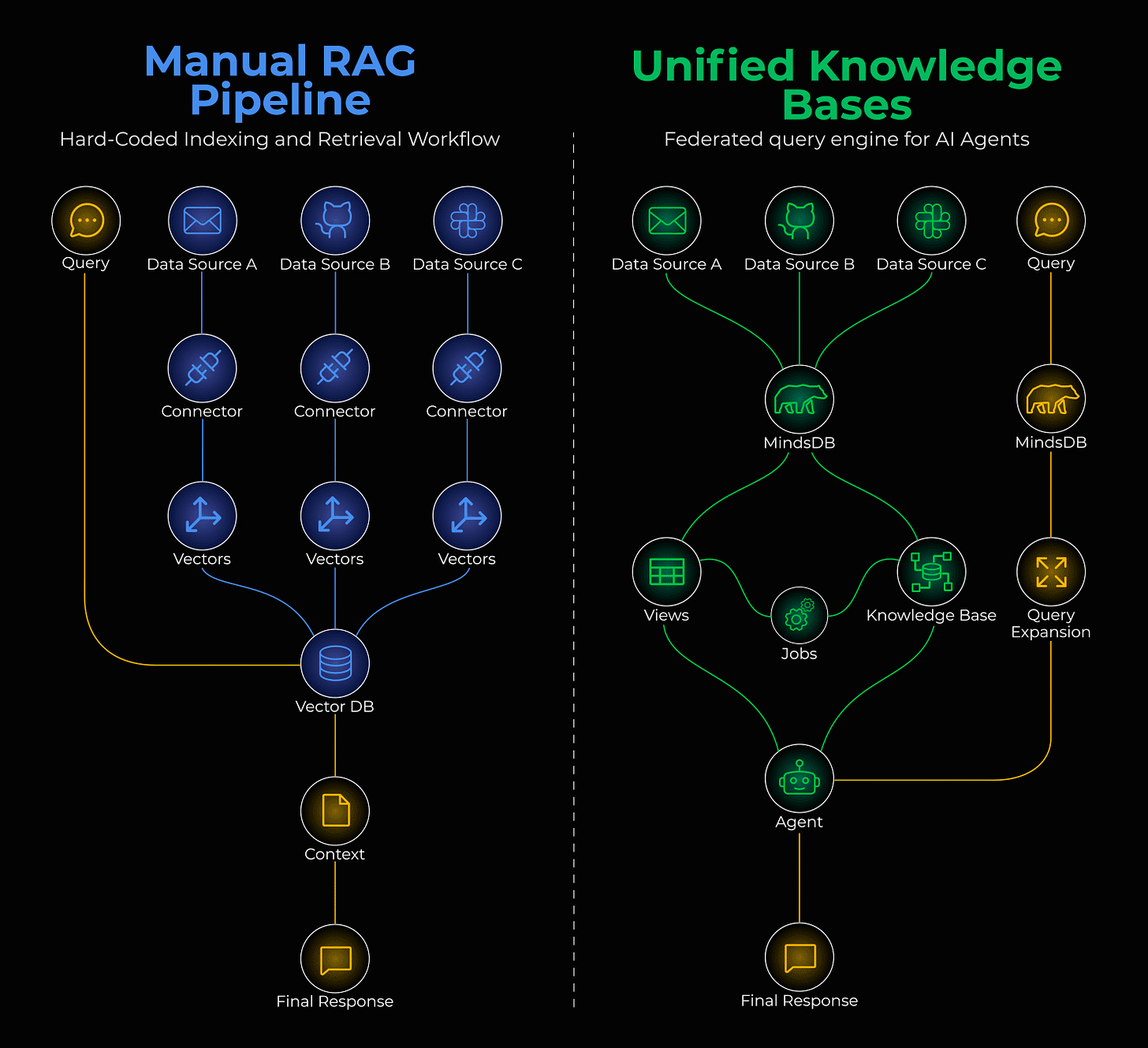
Manual RAG pipeline vs unified knowledge bases
Microsoft.
Google.
AWS.
Everyone’s trying to solve the same problem for AI Agents:
How to connect your agents to enterprise data without duct-taping a dozen tools together?
Enterprise data lives in Postgres, Snowflake, MongoDB, Gmail, etc, scattered across dozens of apps.
The AI logic lives in Python scripts and vector databases.
Building manual RAG pipelines with custom connectors for every data source means you’re already set up for failure.
Here’s an open-source project tackling this differently:
MindsDB treats AI models as virtual tables. Instead of moving data to AI, it brings AI to the data.
The model becomes your table. That’s not a metaphor, that’s literally how it works.
Let’s understand the philosophy of how it works:
↳ Connect: MindsDB federates 200+ data sources. Slack, Salesforce, Gmail - they all become tables you can SELECT from.
↳ Unify: Knowledge Bases and Jobs create an automated semantic layer. Your RAG pipeline runs on SQL, not Python scripts.
↳ Respond: MindsDB acts as an MCP server, so any agent or MCP client can plug in and instantly access your business data.
What does this solve:
Before, you needed a Data Engineer, a Python Engineer, and an MLOps Engineer to build a production RAG system.
With MindsDB, you need a developer proficient in SQL can build, deploy, and automate sophisticated AI agents that learn from live business data.
Intelligence becomes just another database feature.
You can find the MindsDB GitHub repo here →
If you want to see this in action, we have shared a demo below that we covered once in this newsletter before. Continue reading!
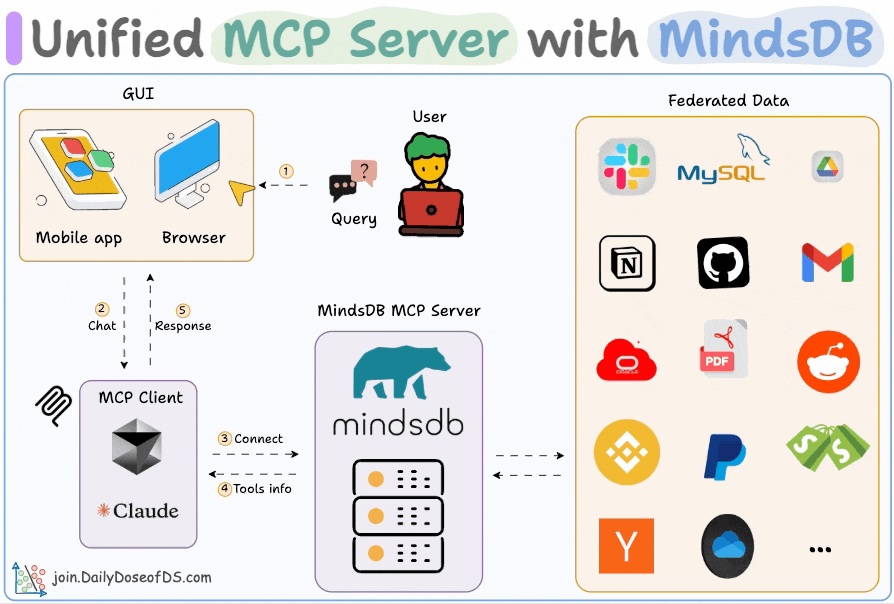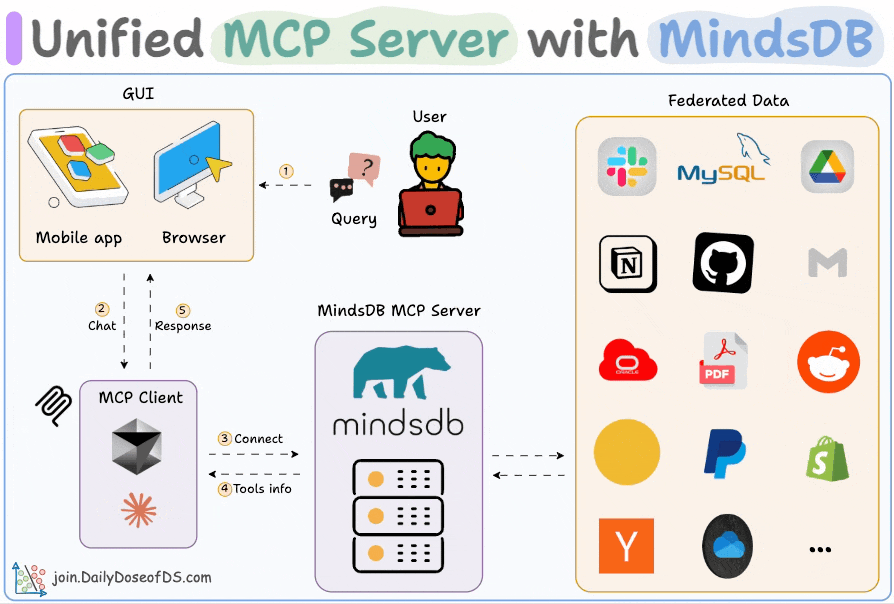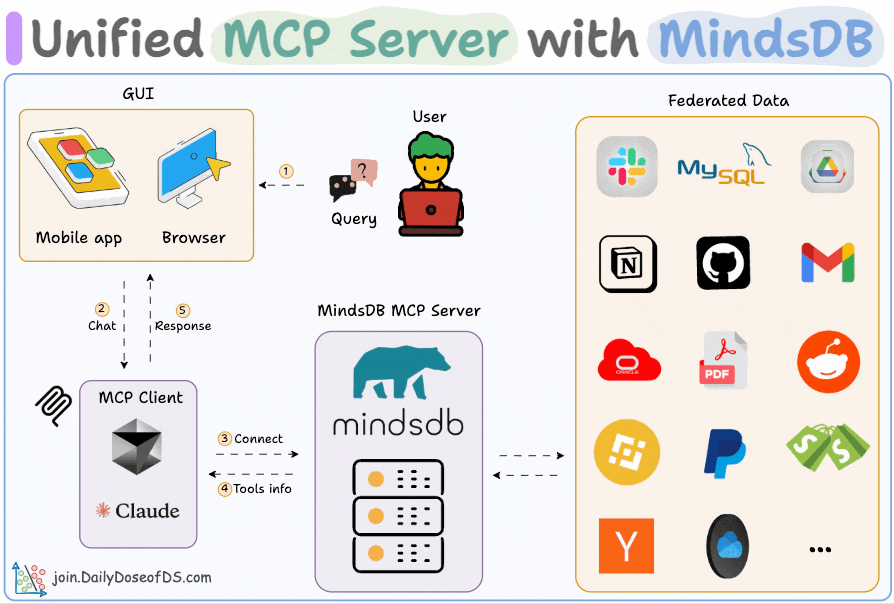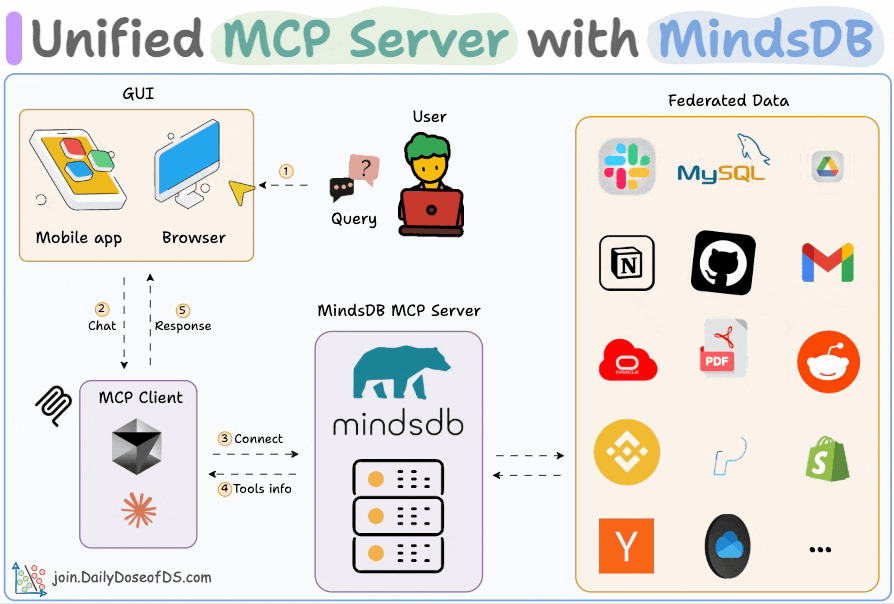
Build an MCP server to connect to 200+ data sources
Organizational data lives everywhere—Slack, Gmail, SQL, Drive, and whatnot!
We built an MCP server that can connect to 200+ such data sources, and it is 100% local.
Our tech stack:
Here’s the workflow:
User submits a query
Agent connects to the MindsDB MCP server to find tools
Agent selects an appropriate tool based on the user query and invokes it
Finally, it returns a contextually relevant response
We have added a video below that gives a complete walkthrough of this demo.
You can find the code to reproduce this demo in the GitHub repo →
Thanks for reading!