Monitoring and Observability in MLOps Lifecycle
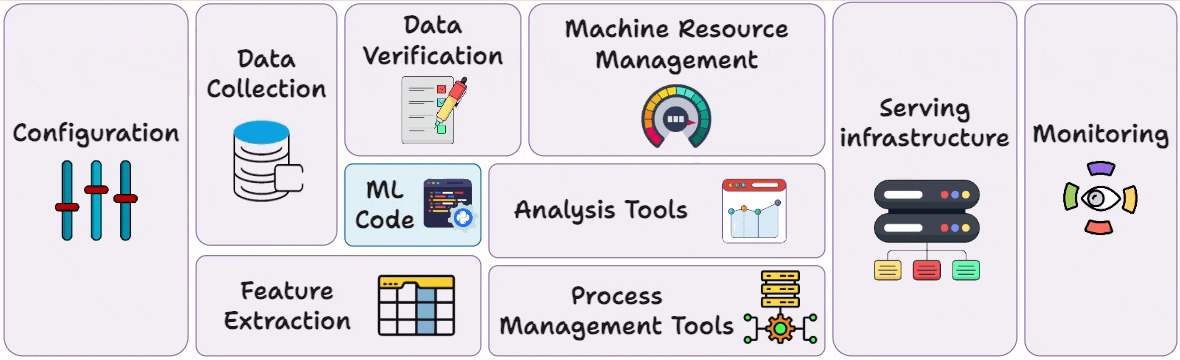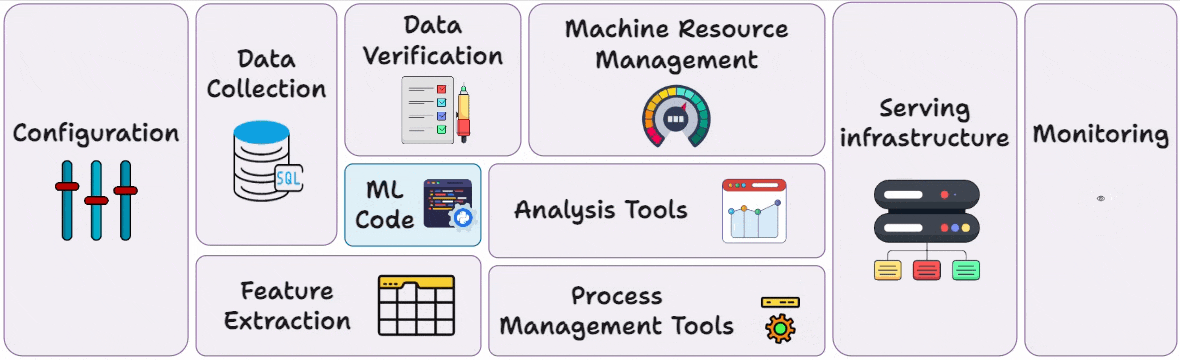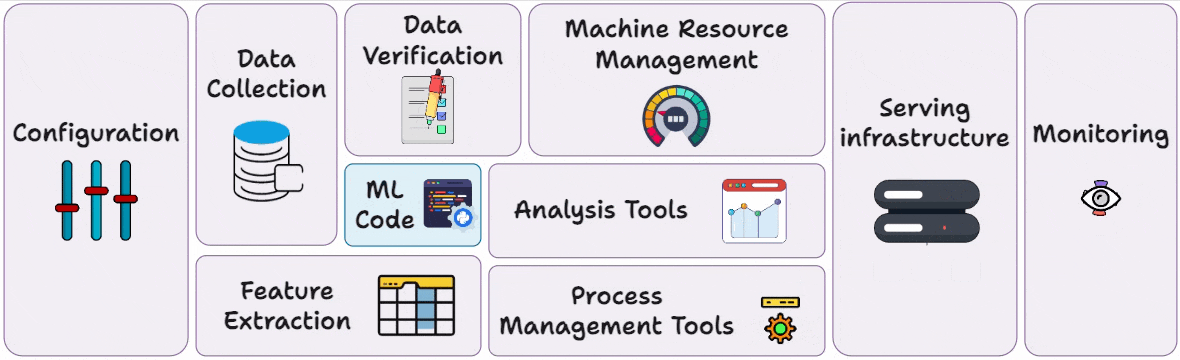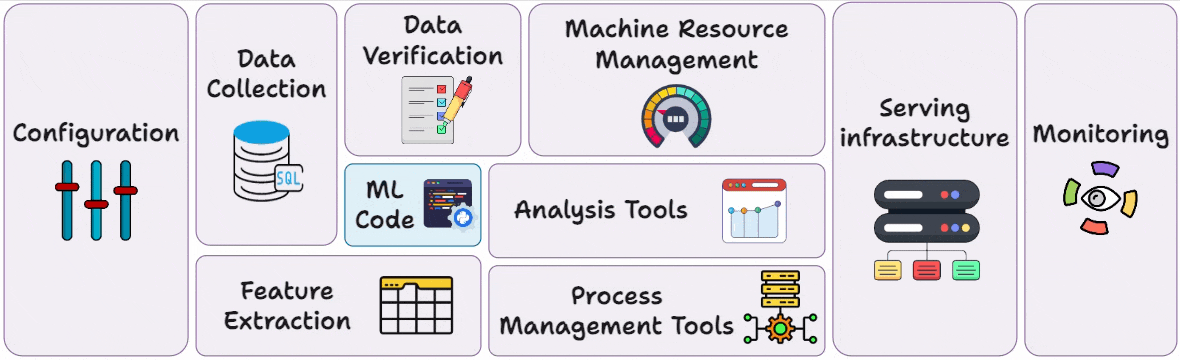
The full MLOps blueprint.
Make Your APIs AI‑Ready in 90 Days
AI‑related API traffic surged 73% in 2024, but most APIs aren’t designed for it.
Postman’s playbook walks you through a 90‑day hands‑on journey:
Days 1-30: Convert messy API docs into machine‑readable formats
Days 31-60: Build infrastructure that supports AI automation
Days 61-90: Deploy AI agents to streamline collaboration at scale
Practical steps to prep your APIs for ML/AI workloads, built by engineers, for engineers.
Thanks to Postman for partnering today!
Monitoring and Observability in MLOps Lifecycle
Part 17 of the MLOps and LLMOps crash course is now available, where we move to the monitoring phase of MLOps and understand the fundamentals of monitoring and observability (with code).
MLOps and LLMOps crash course Part 17 →
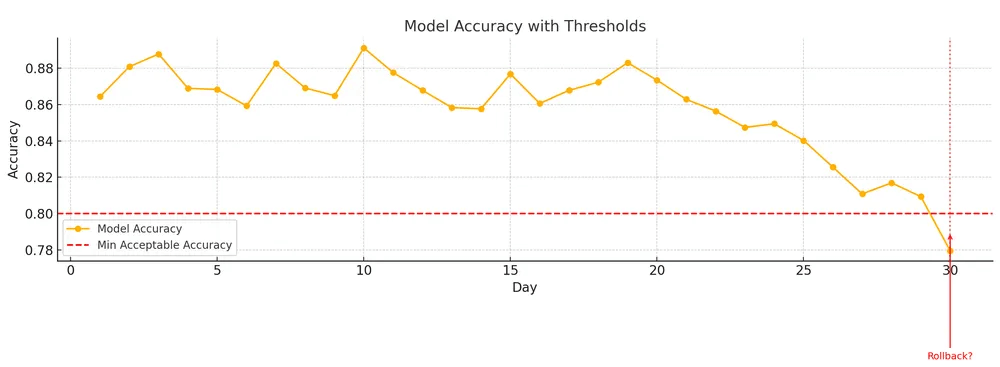
In production, nothing is visible unless you explicitly measure it.
You do not see the input data as it flows through your APIs, and you do not notice drift unless you actively compute it.
A latency spike remains hidden unless you track it, and failures go unnoticed without proper alerting.
Likewise, model degradation stays invisible until logs and metrics expose the underlying issues.
Monitoring is what turns these hidden problems into observable signals you can act upon.
Hence, to prevent any disasters, engineering teams, as per their objectives, adopt a suitable and modern observability stack consisting of Functional monitoring tools and Operational monitoring tools.
Hence, in this and the next few chapters, we’ll discuss everything you need to know about Monitoring and Observability in production, with tooling, like:
Evidently AI
Prometheus
Grafana
and a full hands-on end-to-end ML monitoring demo.
Just like all our past series on MCP, RAG, and AI Agents, this series is both foundational and implementation-heavy, walking you through everything that a real-world ML system entails:
Part 3 covered reproducibility and versioning for ML systems →
Part 4 also covered reproducibility and versioning for ML systems →
Part 7 covered Spark, and orchestration + workflow management →
Part 8 covered the modeling phase of the MLOps lifecycle from a system perspective →
Part 9 covered fine-tuning and model compression/optimization →
Part 10 expanded on the model compression discussed in Part 9 →
Part 11 covered the deployment phase of the MLOps lifecycle →
This MLOps and LLMOps crash course provides a thorough explanation and systems-level thinking to build AI models for production settings.
Just like the MCP crash course, each chapter will clearly explain necessary concepts, provide examples, diagrams, and implementations.
Thanks for reading!