Test Agents Using Agents
...explained with code.
Build Agents that never forget with self-evolving AI memory
Most agents have no real memory. Every conversation starts fresh with no recall of yesterday and no understanding of how information connects.
And here’s where most devs go wrong when trying to fix this: they rely entirely on vector DBs and call it a day.
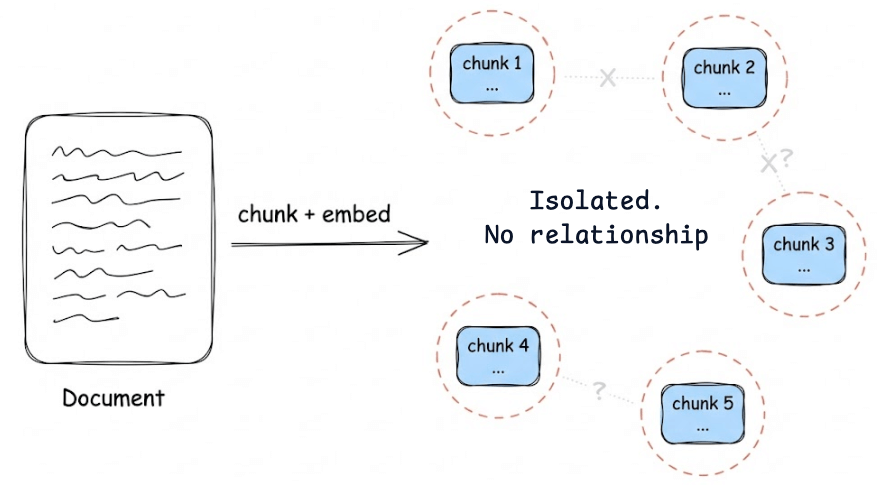
Vector search is fast, but it treats your documents as isolated chunks with no understanding of how they connect. What your agent actually needs is memory that captures relationships and persists over time.
Cognee is an open-source tool built for exactly this.
It combines vector search with graph DBs, making your documents searchable by meaning and connected by relationships.
Here is what makes it even more interesting:
Composable pipelines: Build custom workflows by chaining modular tasks like chunking, embedding, and entity extraction
Weighted memory: Frequently used connections get stronger. Feedback from responses flows back into edge weights, so the graph learns what actually matters.
Self-improving: The Memify pipeline has RL-inspired optimization that strengthens useful paths, prunes stale nodes, and auto-tunes based on real usage.
Getting started with Cognee is as simple as this:
await cognee.add("Your docs here")
await cognee.cognify()
await cognee.memify()
await cognee.search("Your query here")That’s it. Cognee handles the heavy lifting, and your agent geta s memory that actually learns over time.
We’ll cover this in a hands-on demo soon!
Clean ML Datasets With Cleanlab
For the longest time, no one could get past the 91% accuracy on ImageNet (92.4% is quite recent).
This happened because ImageNet had over 100k mislabeled images.
Real-world datasets are messy with noisy labels, missing values, and outliers, which severely degrade your model’s performance.
No sophisticated ML algorithms can compensate for poor-quality data.
Researchers from MIT developed Cleanlab, which is an open-source library that cleans your data in just a few lines of code.
As shown in the image above, Cleanlab can flag errors in any type of data (text, image, tabular, audio), like:
out-of-distribution samples
outliers
label issues
duplicates, etc.
All it takes is just four lines of code:
Import the package.
Pass the dataset and specify the label column.
Find issues by passing the embedding matrix and the probabilities predicted by the model.
Finally, generate the report!
Done!
It will generate a report like the one shown above.
This way, you can easily clean your datasets for training accurate ML models.
Several notebook demos are available here if you want to learn more: Cleanlab demo.
Cleanlab GitHub repo: GitHub repository
How to Test Agents Using Agents
Traditional testing relies on fixed inputs and exact outputs. But agents speak in language, and there’s no single “correct” response.
That’s why we test Agents using other Agents by simulating Users and Judges.
Today, let’s understand Agent Testing by building a pipeline to test Agents with other Agents using Scenario.
Our open-source tech stack:
CrewAI for Agent orchestration.
LangWatch Scenario to build the eval pipeline.
PyTest as the test runner.
Here’s what the process looks like:
1) Define three Agents:
The Agent you want to test.
A User Simulator Agent that acts like a real user.
A Judge Agent for evaluation.
2) Let your Agent and User Simulator Agent interact with each other.
3) Evaluate the exchange using the Judge Agent based on the specified criteria.
Let’s implement this!
Define Planner Crew
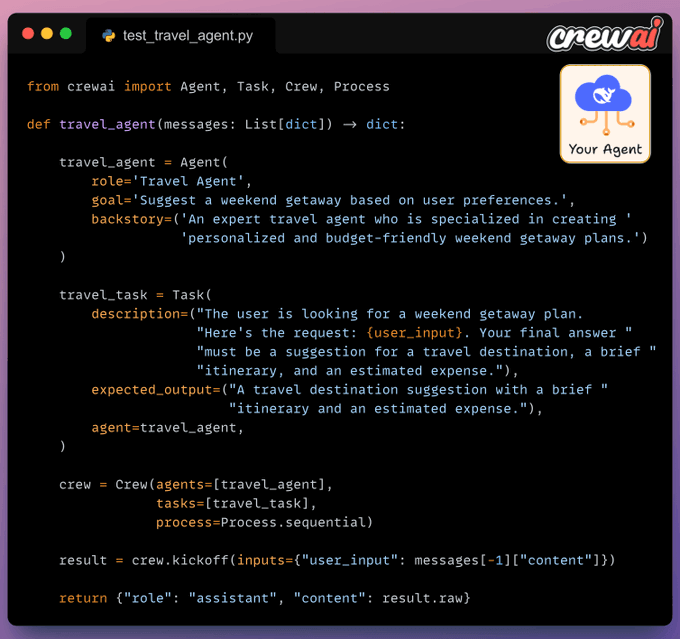
For this demonstration, let’s build a Travel Planner Agent using CrewAI.
It will accept a user query and respond with travel suggestions, a brief itinerary, and an estimated budget.
Configure Crew for testing
In the Scenario library, your Agent class should:
Inherit from the AgentAdapter class.
Define a
call()method that takes the input and returns the output.
Define test
Finally, in our test, we simulate a conversation b/w Travel Agent and User Simulator Agent using the scenario.run method.
After the exchange, a Judge Agent evaluates it using the specified criteria. LangWatch Scenario orchestrates everything!
We specify a name for this test (the
nameparameter).We specify that this test is about (the
descriptionparameter).We specify the agents involved.
Travel Agent: The Agent we want to test.
User Simulator Agent: The Agent that will mimic a real user.
Judge Agent: The Agent that will evaluate the conversation based on the criteria specified in natural language.
Finally, we run the test as follows: uv run pytest -s test_travel_agent.py
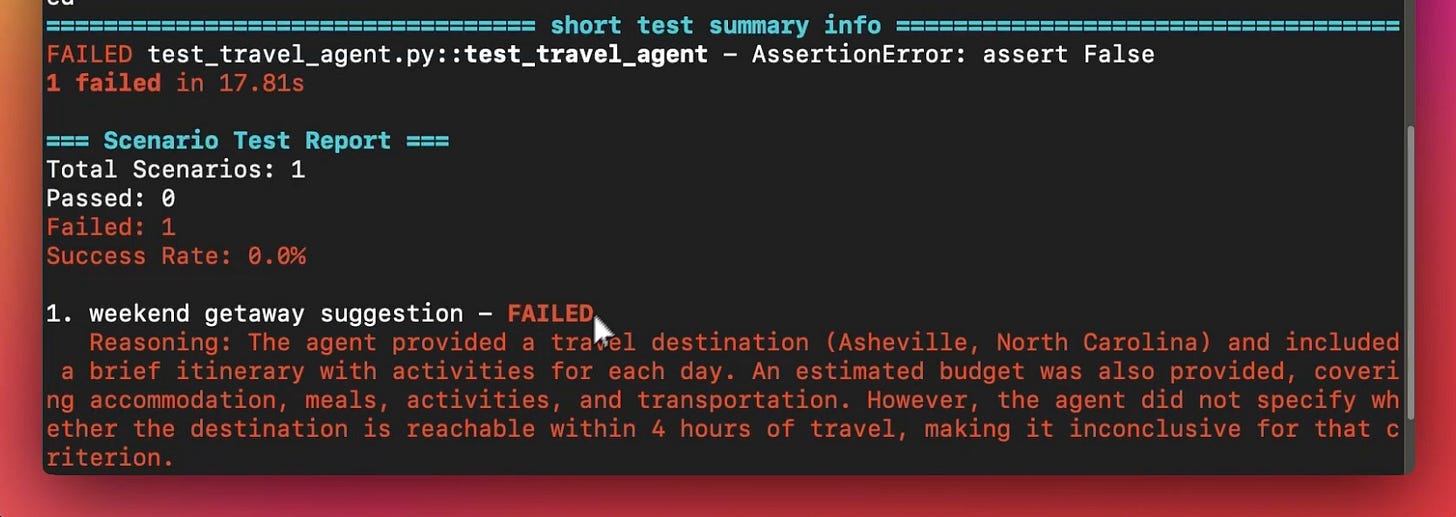
As depicted above, the Judge Agent declared it a failed run since it cannot be determined if the location is <4 hrs away, but this was specified in the criteria when we declared the Judge Agent.
Testing revealed a gap, and we can fix this by prompting the Agent to ask for the location if the user did not specify it.
And that’s how you can build pipelines for Agent testing.
The LangWatch Scenario open-source framework orchestrates this process. It is a library-agnostic Agent testing framework based on simulations.
Thanks for reading!
P.S. For those wanting to develop “Industry ML” expertise:
At the end of the day, all businesses care about impact. That’s it!
Can you reduce costs?
Drive revenue?
Can you scale ML models?
Predict trends before they happen?
We have discussed several other topics (with implementations) that align with such topics.
Here are some of them:
Learn everything about MCPs in this crash course with 9 parts →
Learn how to build Agentic systems in a crash course with 14 parts.
Learn how to build real-world RAG apps and evaluate and scale them in this crash course.
Learn sophisticated graph architectures and how to train them on graph data.
So many real-world NLP systems rely on pairwise context scoring. Learn scalable approaches here.
Learn how to run large models on small devices using Quantization techniques.
Learn how to generate prediction intervals or sets with strong statistical guarantees for increasing trust using Conformal Predictions.
Learn how to identify causal relationships and answer business questions using causal inference in this crash course.
Learn how to scale and implement ML model training in this practical guide.
Learn techniques to reliably test new models in production.
Learn how to build privacy-first ML systems using Federated Learning.
Learn 6 techniques with implementation to compress ML models.
All these resources will help you cultivate key skills that businesses and companies care about the most.