Verbalized Sampling in LLMs
...explained with usage.
Native RAG over Video in just 5 lines of code!
Most RAG systems stop at text.
But a lot of valuable context lives in spoken words and visuals like calls, interviews, demos, and lectures, and it’s tough to build production-grade RAG solutions on them.
Here’s how you can do that in just 5 lines of code with Ragie:
Ingest
.mp4,.wav,.mkv, or 10+ formats.Run a natural language query like “Moments when Messi scored a goal?”
Get the exact timestamp + streamable clip that answers it.
Here’s one of our runs where we gave it a goal compilation video, and it retrieved the correct response:
Top image: ARG vs CRO. It determined there’s a penalty and retrieved the score before and after the penalty.
Bottom image: ARG vs MEX: It fetched the score before the goal and how the goal was scored accurately.
Start building RAG over audio and video here →
Verbalized sampling in LLMs
Post-training alignment methods, such as RLHF, are designed to make LLMs helpful and safe.
However, these methods unintentionally cause a significant drop in output diversity (called mode collapse).
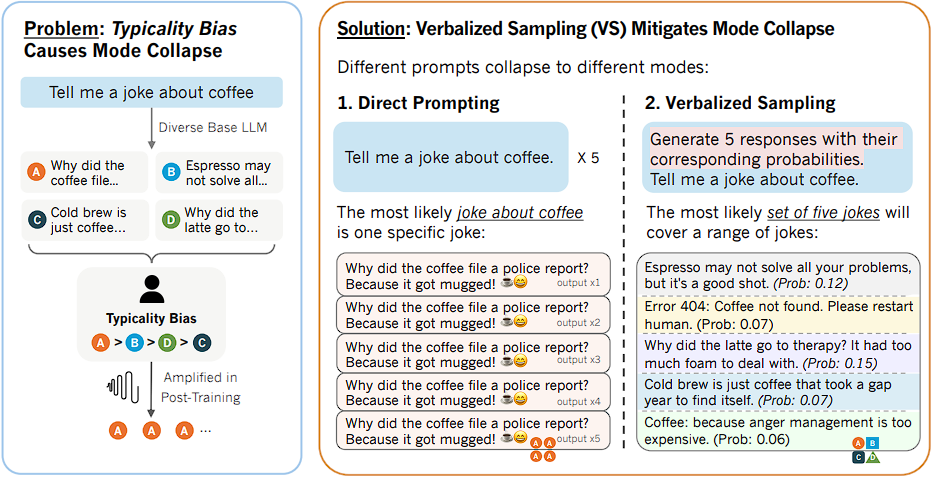
When an LLM collapses to a mode, it starts favoring a narrow set of predictable or stereotypical responses over other outputs.
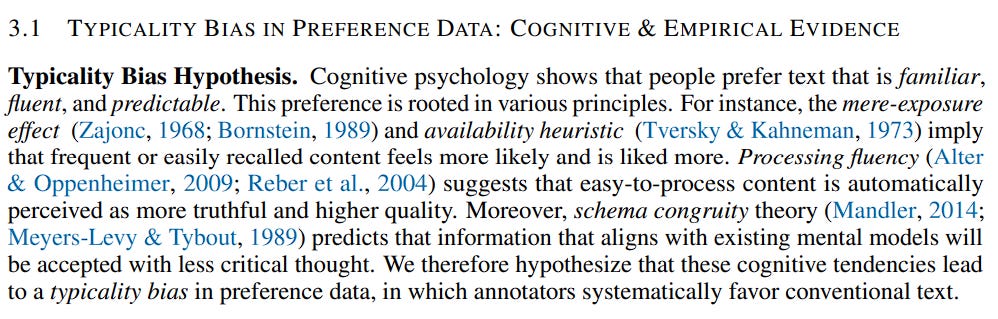
According to a paper, mode collapse happens because the human preference data used to train the LLM has a hidden flaw called typicality bias.
Here’s how this happens:
Annotators are asked to rate different responses from an LLM, and later, the LLM is trained using a reward model that learns to mimic these human preferences.
However, it is observed that annotators naturally tend to favor answers that are more familiar, easy to read, and predictable. This is the typicality bias. So even if a new, creative answer is just as good (or correct) as a common one, the human’s preference often leans toward the common one.
Due to this, the reward model boosts responses that the original (pre-aligned) model already considered likely.
This aggressively sharpens the LLM’s probability distribution, collapsing the model’s creative output to one or two dominant, highly predictable responses.
That said, this is not an irreversible effect, and the LLM still has two personalities after alignment:
The original model that learned the rich possibilities during pre-training.
The safety-focused, post-aligned model [to mention again, due to typicality bias, it had been unintentionally suppressed to strongly favor the most predictable response]
Verbalized sampling (VS) solves this.
It is a training-free prompting strategy introduced to circumvent mode collapse and recover the diverse distribution learned during pre-training.
The core idea of verbalized sampling is that the prompt itself acts like a mental switch.
When you directly prompt “Tell me a joke”, the aligned personality immediately takes over and outputs the most reinforced answer.
But in verbalized sampling, you prompt it with “Generate 5 responses with their corresponding probabilities. Tell me a joke.”
In this case, the prompt does not request an instance, but a distribution.
This causes the aligned model to talk about its full knowledge and is forced to utilize the diverse distribution it learned during pre-training.
So essentially, by asking the LLM to verbalize the probability distribution, the model is able to tap into the broader, diverse set of ideas, which comes from the rich distribution that still exists inside its core pre-trained weights.
Experiments across various tasks demonstrate significant benefits:
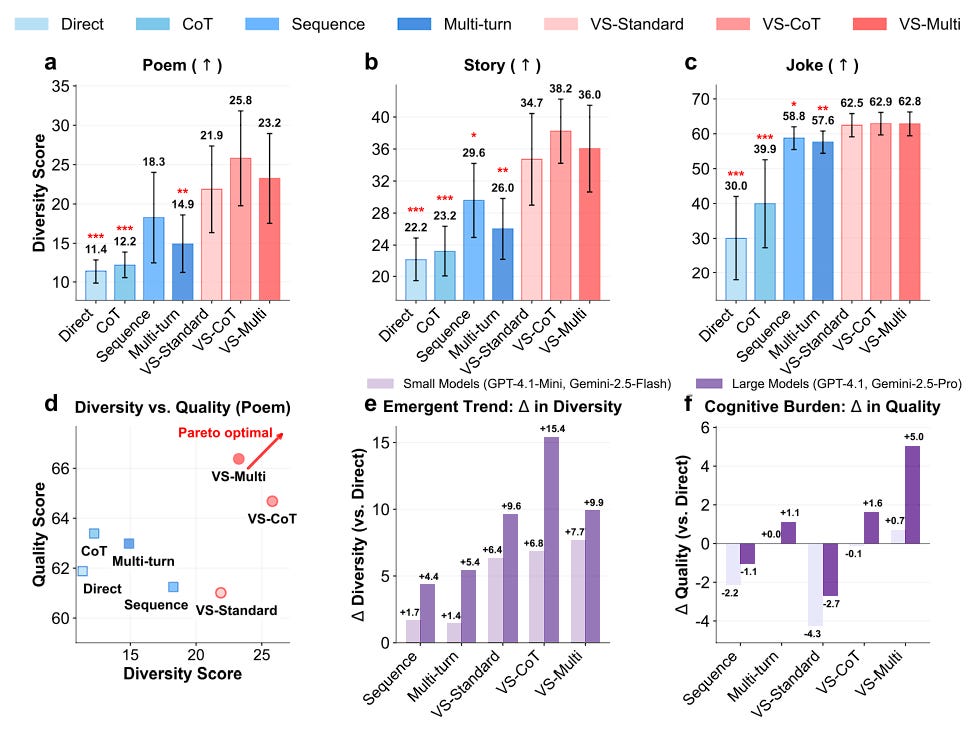
Verbalized sampling significantly enhances diversity by 1.6–2.1x over direct prompting, while maintaining or improving quality. Variants like verbalized sampling-based CoT (Chain-of-Thought) and verbalized sampling-based Multi improve generation diversity even further.
Larger, more capable models like GPT-4.1 and Gemini-2.5-Pro benefit more from Verbalizeb sampling, showing diversity gains up to 2 times greater than smaller models.
Verbalized sampling better retains diversity across post-training stages (SFT, DPO, RLVR), recovering about 66.8% of the base model’s original diversity, compared to a much lower retention rate for direct prompting.
Verbalized sampling’s gains are independent of other methods, meaning it can be combined with techniques like temperature scaling, top-p sampling to achieve further improvements in the diversity-quality trade-off.
👉 Over to you: What other methods can be used to improve LLM diversity?
Thanks for reading!
P.S. For those wanting to develop “Industry ML” expertise:
At the end of the day, all businesses care about impact. That’s it!
Can you reduce costs?
Drive revenue?
Can you scale ML models?
Predict trends before they happen?
We have discussed several other topics (with implementations) that align with such topics.
Here are some of them:
Learn everything about MCPs in this crash course with 9 parts →
Learn how to build Agentic systems in a crash course with 14 parts.
Learn how to build real-world RAG apps and evaluate and scale them in this crash course.
Learn sophisticated graph architectures and how to train them on graph data.
So many real-world NLP systems rely on pairwise context scoring. Learn scalable approaches here.
Learn how to run large models on small devices using Quantization techniques.
Learn how to generate prediction intervals or sets with strong statistical guarantees for increasing trust using Conformal Predictions.
Learn how to identify causal relationships and answer business questions using causal inference in this crash course.
Learn how to scale and implement ML model training in this practical guide.
Learn techniques to reliably test new models in production.
Learn how to build privacy-first ML systems using Federated Learning.
Learn 6 techniques with implementation to compress ML models.
All these resources will help you cultivate key skills that businesses and companies care about the most.